25 Questions
Graphs:
1. Clone Graph
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a value (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; }
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val; // Value of the node
public List<Node> neighbors; // List of neighboring nodes (adjacent nodes)
// Default constructor
public Node() {
val = 0;
neighbors = new ArrayList<Node>();
}
// Constructor to initialize with a value
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
neighbors = new ArrayList<Node>();
}
// Constructor to initialize with a value and a list of neighbors
public Node(int _val, ArrayList<Node> _neighbors) {
val = _val;
neighbors = _neighbors;
}
}
class Solution {
// Recursive DFS method to clone the graph
private Node dfs(Node node, HashMap<Node, Node> oldToNew) {
// Base case: if the node is null, return null
if (node == null) return null;
// If the node has already been copied, return its clone
if (oldToNew.containsKey(node)) {
return oldToNew.get(node);
}
// Create a new node with the same value
Node copy = new Node(node.val);
// Add it to the map before exploring neighbors to handle cycles
oldToNew.put(node, copy);
// Recursively clone all neighbors
for (Node neighbor : node.neighbors) {
copy.neighbors.add(dfs(neighbor, oldToNew));
}
// Return the cloned node
return copy;
}
// Entry method to start cloning the graph
public Node cloneGraph(Node node) {
// HashMap to track original node -> cloned node
HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
// Start DFS cloning from the given node
return dfs(node, map);
}
}
2. Course Schedule
3. 01 Matrix
Given an m x n binary matrix mat, return the distance of the nearest 0 for each cell.
The distance between two cells sharing a common edge is 1.
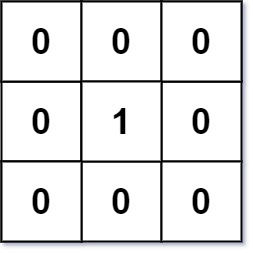
Example 1:
Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]] Output: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
class Solution {
public int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] mat) {
int m = mat.length; // Number of rows
int n = mat[0].length; // Number of columns
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>(); // Queue to perform BFS
// Initialize matrix:
// Add all 0s to the queue and mark all 1s as unvisited (-1)
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(mat[i][j] == 0){
// Add coordinates of 0s to the queue as starting points
queue.add(new int[]{i, j});
} else {
// Mark 1s as -1 to indicate they haven't been processed yet
mat[i][j] = -1;
}
}
}
// Directions to move in the matrix: up, down, left, right
int[][] directions = new int[][]{
{-1, 0}, // Up
{1, 0}, // Down
{0, -1}, // Left
{0, 1} // Right
};
// Perform BFS from all 0s simultaneously
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] curr = queue.poll(); // Current cell coordinates
int currRow = curr[0];
int currCol = curr[1];
// Explore all four directions
for(int[] direction : directions){
int row = currRow + direction[0];
int col = currCol + direction[1];
// Check bounds and whether the cell is unvisited
if(row < 0 || row >= m || col < 0 || col >= n || mat[row][col] != -1){
continue; // Skip invalid or already visited cells
}
// Update the distance and enqueue the cell
mat[row][col] = mat[currRow][currCol] + 1;
queue.add(new int[]{row, col});
}
}
// Return the updated matrix with minimum distances to 0
return mat;
}
}

No Comments