Milestones in the venture building process
In this section we outline key stages entrepreneurs go through when applying the Lean method to build a venture.
Milestones in Venture Building:
The venture building process, when applying the Lean method, involves moving from an idea to a viable venture through several key milestones:
-
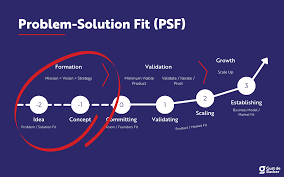
Problem-Solution Fit:
- This is the initial and crucial milestone. At this stage, the entrepreneur determines if they have identified a problem truly "worthy of solving."
- Key questions addressed include: Is it a real problem? Are there enough customers who acknowledge this problem? Is it feasible to solve this problem (economically and technically)?
- Reaching problem-solution fit means validating that a significant number of potential customers acknowledge the problem and would be interested in a solution, and that the proposed solution is achievable at an acceptable price point.
- It's important to remember that at this stage, the idea is still an opinion; validation through Lean tools is essential.
-
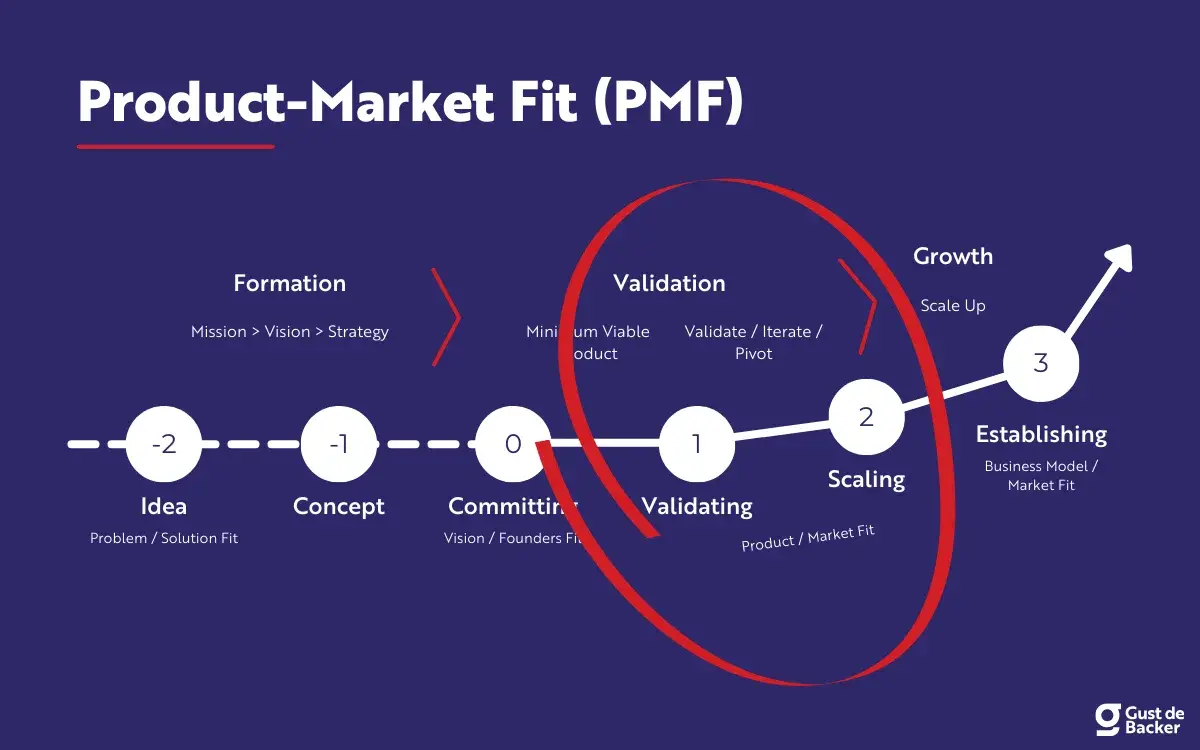
Product-Market Fit (PMF):
- This is the next significant milestone, where the core question is: "Have I built something people want?"
- Unlike problem-solution fit, which can be conceptual, product-market fit involves having a solution (product or service) and validating that customers are willing to pay for it.
- Questions at this stage include: Does the solution effectively address the problem? Is it better than competitors' offerings? Are customers willing to open their wallets and pay for it?
- Achieving PMF signifies that there is a demonstrated demand for the product or service, meaning a product exists, and there is a market for it. This is an exciting point for an entrepreneur as it indicates a good idea and product.
The Iterative Nature of Venture Building:
- The venture building process is not linear. Entrepreneurs may not immediately achieve problem-solution fit, or even after achieving it, they might struggle to find product-market fit. In such cases, it's necessary to loop back to earlier stages, redefine the problem, or rethink the solution.
- External events can also erode product-market fit, forcing a venture to re-evaluate and iterate.
- Product-market fit does not equate to profitability. It simply means there's demonstrated demand and potential for profit because customers are willing to pay. The subsequent stage involves fine-tuning the business model, optimizing costs, improving margins, and scaling the business to achieve sustainability and profitability (e.g., companies like Swiggy or Zomato, while having PMF, are still working towards consistent profitability).
Importance of Customer Focus:
- Early in the process, the primary focus should be on achieving problem-solution fit. This means not immediately obsessing about building the perfect product.
- Customer discovery is a key activity during the problem-solution fit stage, where entrepreneurs identify and understand their potential customers.
- As the venture progresses, customer validation becomes crucial, determining if those customers are truly willing to pay for the solution and at what price.
- The Lean method emphasizes direct engagement with real customers through interviews to gain these insights, rather than relying solely on market research or internal assumptions.
We also set the stage for delving deeper into specific Lean tools like the Lean Canvas, customer development, and the iterative "build-measure-learn" approach to hypothesis testing.