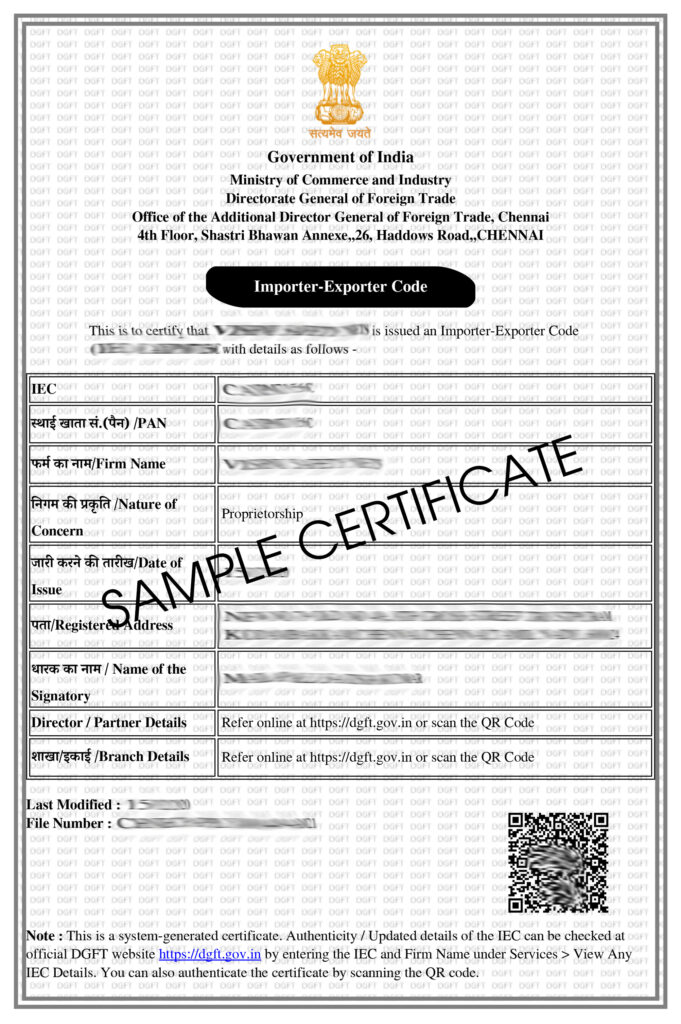
IEC Code
Introduction to Importer-Exporter Code (IEC) in India
These notes provide a comprehensive overview of the Importer-Exporter Code (IEC) in India, explaining its definition, importance, application process, and related aspects with examples where applicable.
What is an IEC Code?
-
Definition: The IEC (Importer-Exporter Code) is a 10-digit unique code issued by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT), which is part of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry in India. This code serves as the primary identification for businesses engaged in import and export activities.
-
Applicability: It's mandatory for any business in India that wishes to participate in international trade, meaning both import and export of goods or services. If your business involves either bringing goods into India from another country or sending goods out of India to another country, you need an IEC.
-
Validity: The IEC code is valid for the lifetime of the business, which means it doesn't require renewal. Once you have the code, it remains valid unless there's a change in the legal entity or business structure.
Why is the IEC Code Important?
-
Legal Requirement: Obtaining an IEC is a legal mandate for importing or exporting goods from India. No international trade can be legally conducted without this code. Think of it as a permit to participate in global trade.
-
Business Identification in Global Trade: The IEC acts as an identification number for businesses engaged in international trade, similar to how a Tax Identification Number (TIN) is for domestic tax purposes. It allows for the proper tracking and documentation of all international trade activities.
- Example: When a business ships a consignment internationally, the IEC number needs to be mentioned on customs documentation, making the business easily identifiable.
-
Accessing Export Benefits & Incentives: The Indian government offers various export benefits and incentives to encourage exports, such as duty drawbacks, subsidies, and tax exemptions. To avail of these incentives, the IEC code is a primary requirement.
- Example: A textile exporter needs an IEC code to claim duty drawback on the taxes paid on raw materials used in manufacturing the exported goods.
-
Compliance with Government Regulations: Having an IEC ensures that a business is compliant with government regulations related to import and export. This compliance helps in avoiding legal issues and penalties.
Benefits of Having an IEC Code
-
Facilitates Global Business: An IEC is the key to unlocking international markets, allowing businesses to expand their reach and tap into global demand.
- Example: A small handicraft business in India can start exporting its goods to other countries, significantly increasing its potential customer base.
-
Ease of Customs Clearance: The IEC code is essential for customs documentation. Without it, customs authorities will not clear goods for import or export, causing delays and potential losses.
- Example: An importer needs to declare their IEC code for the goods being imported to clear Indian customs and be released.
-
Government Incentives: With an IEC, businesses can access various export subsidies and duty exemptions, reducing their costs and improving competitiveness.
- Example: Businesses can claim subsidies under the Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS) using their IEC.
-
No Annual Compliance: Unlike other business registrations, the IEC code doesn't require annual renewal or compliance formalities, simplifying the process for exporters. However, annual updates are now required to confirm business information.
Eligibility Criteria for IEC
-
Who Can Apply: Individuals, companies, firms, and any business entity involved in international trade activities can apply for an IEC code.
-
Mandatory PAN Card: A Permanent Account Number (PAN) card of the business entity (sole proprietor, company, partnership firm) is mandatory for obtaining an IEC. The PAN is the link to the business’s tax information.
-
Valid Bank Account: The business entity must possess a valid bank account in its name. This account is necessary for all trade transactions and will be used for financial transactions related to import and export.
How to Apply for an IEC Code
-
Visit the DGFT Website: Go to the official DGFT (Directorate General of Foreign Trade) website: www.dgft.gov.in.
-
Fill the Application Form (Form ANF 2A): Download and fill out the online application form, Form ANF 2A, which includes necessary details about the business.
-
Attach Required Documents: Upload scanned copies of the following documents:
- PAN Card Copy: PAN card of the individual or company.
- Address Proof: Valid address proof of the business premises. This could be a utility bill, rental agreement, or property tax receipt.
- Cancelled Cheque or Bank Certificate: Cancelled cheque or a bank certificate that confirms the bank details of the business.
-
Pay the Registration Fee Online: Pay the registration fee online through the payment gateway provided on the DGFT website. This fee is nominal.
-
Receive IEC Code: After verification of the application and supporting documents, the IEC code will be issued and sent to the applicant via email.
Documents Required for IEC Application
-
PAN Card (Individual/Company): Self-attested copy of PAN Card.
-
Aadhaar Card (for Proprietorship): Self-attested copy of the proprietor's Aadhaar Card.
-
Business Incorporation Certificate: Certificate of Incorporation for companies or registration documents for partnership firms.
-
Address Proof of Business Premises: Utility bill, property tax receipt, or rental agreement in the name of the business.
-
Bank Details: A cancelled cheque or a bank statement in the name of the business, showing the account number and the name of the account holder.
IEC and GST Integration
-
Linking IEC with GSTIN: Businesses registered under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime need to link their IEC code with their GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number). This ensures smooth compliance and efficient tracking of trade data.
-
Simplifies Tax Compliance: This integration streamlines tax compliance for businesses involved in international trade, as all trade and tax data are linked.
Exemptions from IEC Code
-
Personal Use Imports/Exports: Individuals importing or exporting goods for personal use (not for commercial purposes) are generally exempt from needing an IEC code.
- Example: An individual buying clothes online from another country for personal use doesn't need an IEC.
-
Central/State Government Departments: Central and state government departments are typically exempt from obtaining an IEC.
-
Ministries and Notified Charitable Organizations: Certain ministries and notified charitable organizations are also exempted.
Role of IEC in Export
-
Identification for Exporters: The IEC serves as the primary identification for all export transactions, ensuring proper documentation and tracking.
-
Customs Clearance: The IEC is crucial for completing all customs procedures and documentation for exporting goods.
-
Incentives and Benefits: Enables exporters to claim government incentives like duty drawbacks, subsidies, and other export-related benefits.
-
Global Reach: Facilitates easier entry into international markets by ensuring compliance with global trade standards and norms.
Role of IEC in Import
-
Customs Requirement: An IEC is essential for clearing imported goods at Indian ports.
-
Foreign Currency Transactions: Facilitates opening and maintaining foreign currency accounts to make import payments.
-
Compliance with Trade Regulations: Helps importers to adhere to various trade and taxation laws and regulations.
-
Access to Concessions: Enables importers to avail reduced duties under Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with other countries.
Compliance with IEC
-
Updates and Modifications:
- Businesses are required to update their IEC details in case of any changes in the business name, address, or the nature of their business.
- These updates are done online via the DGFT portal.
-
Annual Updates:
- Businesses are now required to confirm their IEC details annually through an online portal. This keeps the information up-to-date and accurate.
-
Digital Signature Integration:
- Linking the IEC with a digital signature ensures secure online transactions related to import/export, providing an added layer of security and compliance.
Challenges in IEC Application
- Errors in Application: Incorrectly filled application forms or submission of wrong documents can lead to the rejection of the IEC application.
- Lack of Awareness: Many small businesses and MSMEs are not aware of the importance, necessity, and benefits of having an IEC.
- Technical Glitches: The online application process on the DGFT portal can sometimes have technical glitches, causing inconvenience.
- Language Barriers: Limited assistance for non-English speaking applicants can pose a challenge.
Government Initiatives for Ease of IEC
- Online Application System: A simplified online application system through the DGFT portal has made the process more efficient.
- Integration with GST and Customs: Streamlined processes through integration with GST and customs authorities have reduced paperwork and delays.
- Support for MSMEs: Special awareness programs and assistance for small and medium enterprises are conducted to encourage them to engage in international trade.
- Trade Facilitation Schemes: Various government schemes are designed to promote and simplify export-import operations, easing the process for businesses.
Summary
- Gateway to International Trade: IEC is the essential gateway for Indian businesses to participate in international trade activities.
- Ensures Compliance: IEC ensures compliance with trade laws and facilitates smoother customs clearance processes.
- Key to Incentives: The IEC code plays a pivotal role in availing various export incentives and duty benefits provided by the government.
- Accessible and Efficient: Government initiatives have significantly streamlined and made the IEC application process more accessible and efficient, encouraging more businesses to engage in global trade.