Financial instruments in capital markets :shares ,mutual funds , debentures ,bonds
- Mutual Funds:
Definition:
Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of securities (stocks, bonds, etc.).
Key Features:
Diversification, reducing risk.
Professional management.
Liquidity (shares can be redeemed).
Various types of mutual funds catering to different investment goals (e.g., equity funds, debt funds).
Role:
Provide investors with access to diversified portfolios.
Enable investors to participate in markets with smaller investments. 3.
- Debentures:
Definition:
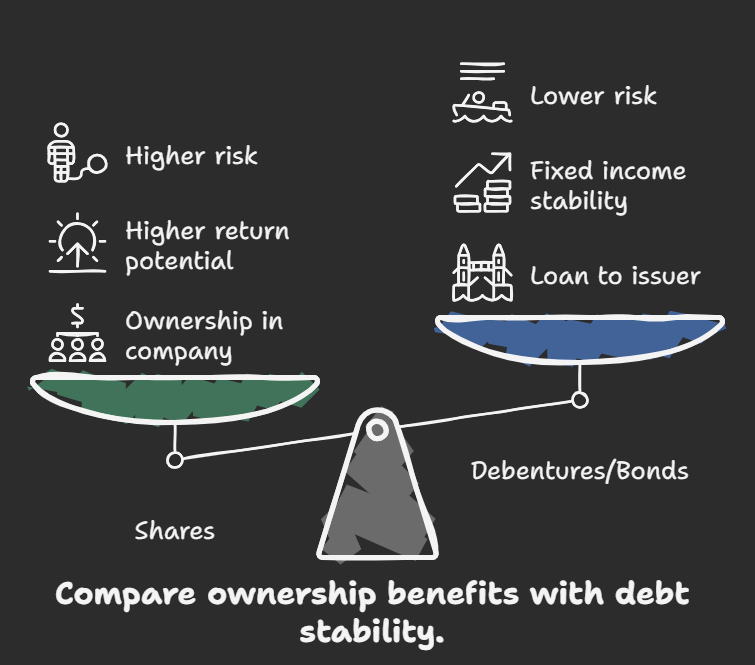
Debentures are debt instruments issued by corporations to raise capital. They represent a loan from the investor to the company.
Key Features:
Fixed interest payments.
Typically unsecured (not backed by specific assets).
Represent a debt obligation of the company.
Generally considered less risky than shares but riskier than secured bonds.
Role:
Companies use debentures to raise debt capital.
Investors use debentures to earn fixed income. 4.
- Bonds:
Definition: Bonds are debt instruments issued by governments, municipalities, or corporations. They represent a loan from the investor to the issuer. Key Features: Fixed interest payments (coupon payments). Principal repayment at maturity. Can be secured (backed by assets) or unsecured. Varying levels of risk depending on the issuer's creditworthiness. Role: Governments and corporations use bonds to raise debt capital. Investors use bonds to earn fixed income and preserve capital. Key Differences: