Other sources of finance
Bootstrapping is the process of starting and growing a business using your own resources, rather than relying on external funding like investors or loans. It's a common path for many early-stage startups, and it offers a lot of control and flexibility.
What is Bootstrapping?
Think of it like pulling yourself up by your own bootstraps (hence the name!). It means you're funding your business with:
- Your Savings: Money you've personally saved.
- Revenue from Sales: Money you earn by selling your product or service.
- Sweat Equity: Your own hard work and the hard work of your co-founders, often with little or no salary initially.
- Minimal Expenses: Keeping costs as low as possible.
Key Advantages of Bootstrapping:
- Control: You retain complete ownership and decision-making power. You're not beholden to investors who might have different ideas.
- Flexibility: You can pivot or change direction more easily since you don't need to get approval from investors.
- Focus on Profitability: Bootstrapping forces you to focus on generating revenue and becoming profitable early.
- Strong Work Ethic: It often requires a strong commitment and work ethic, which can build a great foundation for your business.
- Higher Potential Returns: If you are successful, you get to keep a larger share of the profits, since you haven't given away equity to investors.
Challenges of Bootstrapping:
- Limited Resources: You'll likely have less cash to work with, which can make it harder to hire talent or scale quickly.
- Slower Growth: You might grow slower than a company that raises external funding.
- Personal Risk: Your personal savings and time are at risk.
- More Demanding: You'll likely be wearing many hats and working long hours.
- Cash Flow Management: You'll need to be very careful with managing your cash flow.
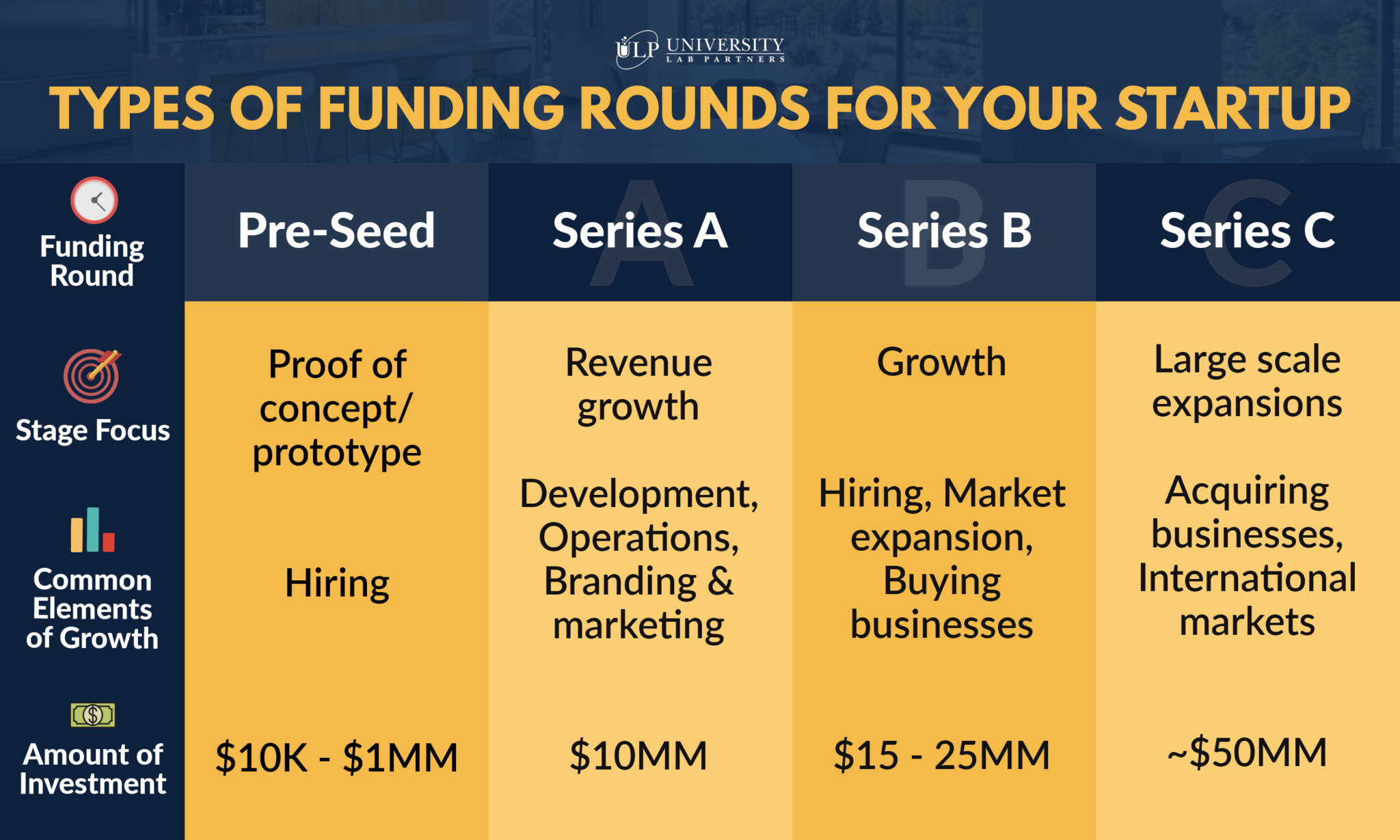
Series Funding: An Alternative to Bootstrapping
Series funding refers to the rounds of investment that a startup receives from external investors (typically venture capital firms) as it grows. Unlike bootstrapping, this route means giving up some equity (ownership) in exchange for capital. Here's a simple breakdown:
Common Series Rounds:
- Seed Funding: Typically the first round of funding, often used to develop a product, validate the market, and build a basic team.
- Series A: Used for early-stage scaling, hiring a larger team, and expanding your market reach.
- Series B: Used for further growth, scaling operations, and expanding into new markets.
- Series C and Beyond: Later-stage rounds used for rapid expansion, acquisitions, and preparing for a potential IPO (Initial Public Offering).
Key Differences Between Bootstrapping and Series Funding:
| Feature | Bootstrapping | Series Funding |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Personal savings, revenue | External investors (VCs, etc.) |
| Ownership | Retain full ownership | Give up equity (ownership) |
| Control | Full control | Shared control with investors |
| Growth Pace | Potentially slower | Potentially faster |
| Risk | Higher personal risk | Lower personal risk |
| Profitability | Focus on early profitability | Might prioritize growth over profit |
Choosing the Right Path
There's no one-size-fits-all answer. Here's how to think about it:
-
Bootstrapping is good if:
- You value control and independence.
- You have a clear vision and are comfortable being frugal.
- Your business doesn't require massive upfront capital.
- You are willing to work hard and take on significant personal risk.
-
Series Funding is good if:
- Your business needs significant capital to scale quickly.
- You're willing to share control and equity with investors.
- You have a clear path to rapid growth and market dominance.
- You can attract and convince investors of your potential.