Country Risk Analysis
Country Risk Analysis
What is Country Risk?
- Definition: The risk associated with investing or doing business in a particular country, encompassing the potential for losses due to factors specific to that country.
- Key Aspect: Goes beyond standard business risk; involves factors at a national level that can impact investments or operations.
- Why it Matters: Informs decisions on international investment, trade, and lending; essential for risk management.
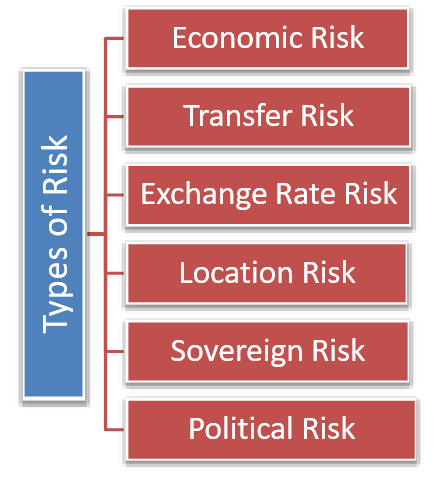
Types of Country Risk:
-
Political Risk:
- Definition: The risk that political events or government actions in a country will negatively affect a business or investment.
- Focus: Factors relating to the stability and policies of a government.
-
Economic Risk:
- Definition: The risk that a country's economic conditions will negatively affect a business or investment.
- Focus: Factors relating to the health and performance of a country's economy.
-
Transfer Risk:
- Definition: The risk that a government will restrict the movement of capital in or out of the country.
- Focus: The ability to convert a profit in local currency into a foreign currency
-
Sovereign Risk:
- Definition: The risk that a government will default on its debts or fail to meet its financial obligations.
- Focus: A countries ability to meet its financial obligations.
-
Operational Risk:
- Definition: The risk that business operations will be disrupted due to inefficiencies or shortcomings in a country
- Focus: The challenges of operating a business in a different country.
Measuring Political Risk
Key Areas to Assess:
-
Political Stability:
- Factors: Government structure, history of political transitions, strength of democratic institutions, levels of corruption, social unrest, and likelihood of conflict/civil war.
- Indicators: Political stability ratings, corruption perception indices, freedom of press rankings, measures of civil liberties, levels of violence.
- Importance: High instability can lead to business disruptions, policy changes, and even nationalization.
-
Government Effectiveness:
- Factors: Quality of public services, regulatory environment, level of bureaucracy, rule of law, effectiveness of the judiciary, strength of property rights.
- Indicators: World Bank governance indicators, business environment rankings, ease of doing business scores, level of corruption.
- Importance: Ineffective governments can lead to inefficient operations, increased costs, and risks to property and contracts.
-
Ideology and Policies:
- Factors: Political ideology of the ruling party, level of intervention in the economy, policies on nationalization, trade restrictions, price controls, and taxation.
- Indicators: Government policy statements, legal frameworks, regulatory changes, levels of trade protectionism.
- Importance: Changes in policies can radically impact business operations and profitability.
-
Geopolitical Risks:
- Factors: Relations with neighbouring countries, international alliances, involvement in international disputes, and likelihood of sanctions.
- Indicators: International relations index, reports on international disputes, sanctions list.
- Importance: Political or military disputes can have a strong impact on domestic trade and investment.
Underlying Economic and Political Factors
Economic Factors:
-
Economic Growth:
- Impact: High growth can create opportunities, while low growth can reduce profitability and lead to social unrest.
- Indicators: GDP growth, inflation rates, unemployment rates, level of public debt.
-
Economic Stability:
- Impact: High inflation, volatile exchange rates, and large budget deficits can negatively impact businesses and investment returns.
- Indicators: Inflation rates, exchange rate volatility, balance of payments data, government budget deficits.
-
Market Characteristics:
- Impact: Market size, income levels, income inequality, and quality of infrastructure can affect market access and profitability.
- Indicators: Market size, GDP per capita, Gini coefficient, infrastructure quality rankings.
-
Fiscal and Monetary Policy:
- Impact: Government spending and taxation policies can have an effect on overall economic activity and borrowing costs.
- Indicators: Levels of taxation and government expenditure, interest rates.
Political Factors:
-
Political Ideology:
- Impact: The ruling party’s ideology (e.g., socialist, capitalist) influences policies and regulations.
- Indicators: Government statements, policy documents, historical political patterns.
-
Legal and Regulatory Framework:
- Impact: Transparent and reliable legal systems protect property rights, enforce contracts and provide an environment conducive to investment.
- Indicators: Rule of law rankings, contract enforcement data, property rights protection rankings.
-
Corruption:
- Impact: High levels of corruption increase costs, risks, and uncertainty.
- Indicators: Corruption perception indices, bribery rates.
-
Social Stability:
- Impact: Social unrest, inequality, or ethnic tensions can lead to disruptions and political instability.
- Indicators: Social unrest reports, human rights rankings, levels of income inequality.
How to Assess Country Risk:
- Qualitative Analysis: Involves expert assessments, interviews, and reading news reports to analyse political and social situations.
- Quantitative Analysis: Involves the use of numerical data and indicators to create scores and rankings of countries.
- Scenario Analysis: Planning for various potential outcomes and risk events.
- Risk Rating Agencies: Using established risk ratings and country reports from agencies like Moody's, Standard & Poor's, and Fitch.
- Diversification: Reduce risk by investing across multiple countries.
In Summary
Country risk analysis is crucial for international business decisions. Political risk, driven by a combination of underlying political and economic factors, significantly affects business operations and profitability. Careful analysis using both qualitative and quantitative methods is essential for effective risk management.