SEO Fundamentals
Introduction to SEO and SEM: What's the Difference?
Defining Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is not some magical trick; it's a deliberate process. Think of it as meticulously crafting your website to be the perfect answer to a search engine's question.
SEO fundamentally means optimizing a website's:
- Technical Configuration: This is the foundation. It involves ensuring your site is easily crawlable, indexable, and fast.
- Content Relevance: Providing valuable, informative, and engaging content that perfectly matches what users are searching for.
- Link Popularity (Authority): Earning backlinks from other reputable websites, signaling that your site is a trusted source of information.
In essence, SEO aims to improve your website so it becomes:
- Easily Findable: When someone types a query into Google, your site is a top result.
- More Relevant: Your content accurately answers the user's question and provides value.
- Popular: Your site is seen as a trusted source of information in its niche.
The ultimate goal is to make search engines (like Google) recognize your site as the best option for a particular search query, leading to higher rankings.
How SEO Optimizes a Website: A Multi-Faceted Approach
SEO isn't just one thing; it's a combination of strategies that work together. Here are the core components:
-
Technical SEO: This is the behind-the-scenes work that makes your website easily accessible to search engines.
- Example: Making sure your website loads quickly on all devices, has a clear site structure (sitemap), and doesn't have broken links.
-
On-Page SEO: Optimizing the visible elements of your web pages to improve relevance and user experience.
- Example: Writing compelling title tags and meta descriptions that entice users to click, using relevant keywords naturally in your content, and organizing your content with clear headings.
-
Off-Page SEO: Building your website's authority and reputation through activities outside your website.
- Example: Earning backlinks from reputable websites in your industry, engaging on social media, and building brand mentions.
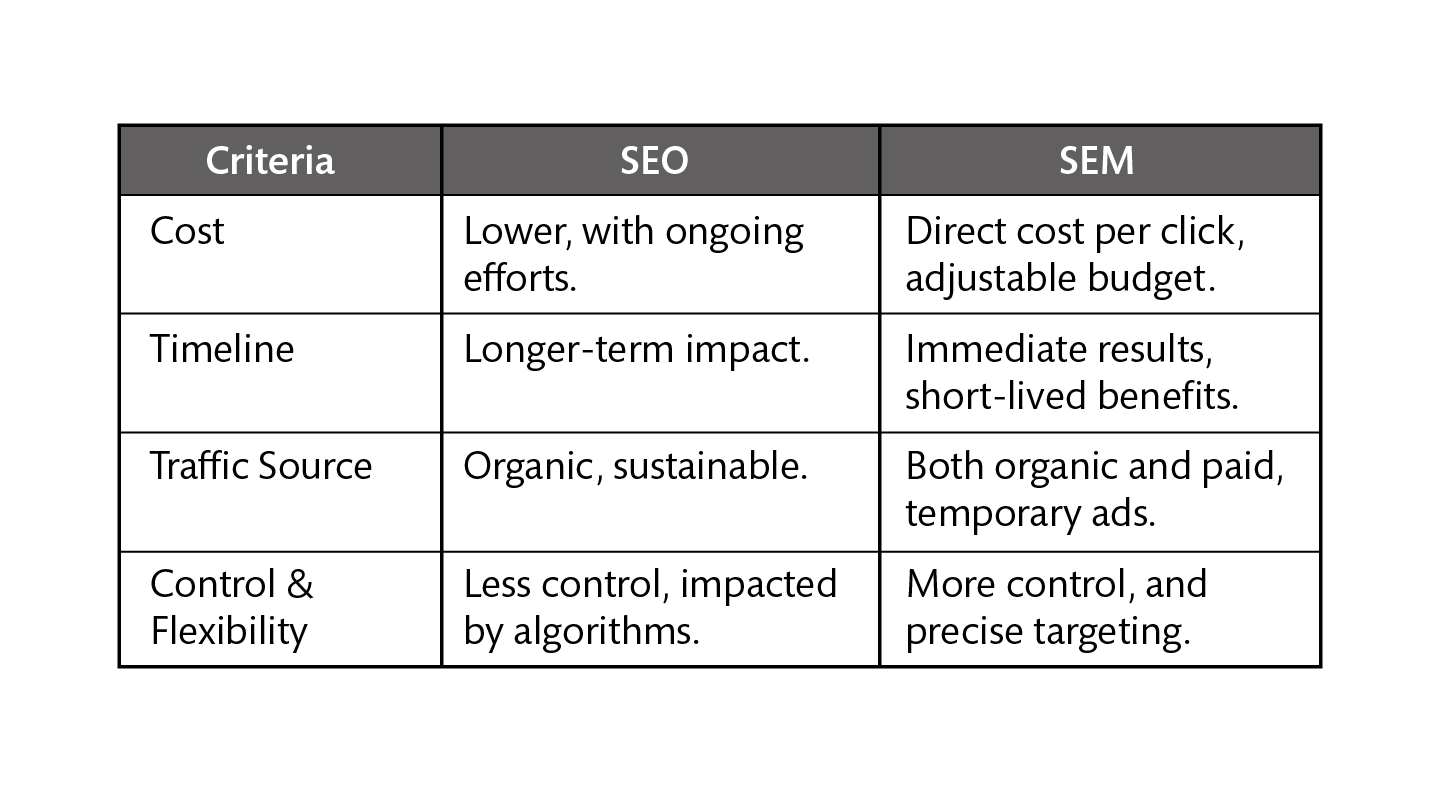
SEO vs. SEM: Untangling the Terminology
It's easy to confuse SEO and SEM (Search Engine Marketing). Here's a breakdown of the key differences:
| Feature | SEO (Search Engine Optimization) | SEM (Search Engine Marketing) |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Organic (unpaid) | Paid and Organic |
| Focus | Improving organic rankings to increase visibility from organic search | Driving traffic and visibility from all search sources (paid & organic) |
| Cost | Primarily cost-effective, focusing on time and effort. | Involves advertising costs (e.g., Google Ads). |
| Speed of Results | Results typically take time (months) to see significant changes. | Faster results can be achieved using paid advertising. |
In simpler terms:
- SEO is like planting a garden: You carefully cultivate your website (content, technical aspects, etc.) and wait for it to grow and attract visitors organically.
- SEM is like renting a billboard: You pay to get your message in front of people immediately.
Real-Life Business Example: The Delicious Delights Bakery
-
Scenario: A local bakery wants to attract more customers.
-
SEO Approach:
- "Delicious Delights Bakery" optimizes its website with keywords like "best bakery in [city]," "custom cakes [city]," and "fresh pastries."
- They create a blog with recipes and articles about baking, targeting relevant searches (e.g., "how to make chocolate frosting").
- They ensure their website is mobile-friendly and loads quickly.
- They build local citations (listings) on websites like Yelp, Google Maps, and local directories.
- They build a good reputation for customer reviews.
-
SEM Approach:
- Alongside the SEO efforts, "Delicious Delights Bakery" runs Google Ads targeting searches for "bakery near me," "birthday cakes [city]," and other relevant keywords.
- They might offer a special discount coupon in their ads to entice clicks and conversions.
-
Key Takeaway: SEM encompasses both paid advertising and organic SEO. SEO is part of SEM.
The Power of Keyword Optimization: Connecting with Your Audience
Keywords are the bridge between what people search for and the content you provide. Keyword optimization is the process of strategically incorporating relevant keywords throughout your website to improve its visibility for those searches.
Think of keywords as the language your target audience uses to find what they're looking for. By understanding this language and using it effectively on your website, you increase the chances of attracting the right visitors.
Real-Life Business Example Company: Amazon
Strategy: Amazon's success relies heavily on mastering keyword optimization. Imagine searching for a "wireless Bluetooth speaker."
- Keyword Research: Amazon identifies keywords their audience uses (e.g., "portable speaker," "Bluetooth speaker," "waterproof speaker").
-
Optimization: They incorporate these keywords in:
- Product Titles: "JBL Flip 6 Portable Waterproof Bluetooth Speaker"
- Product Descriptions: Highlighting features that match common searches (e.g., "long battery life," "deep bass").
- Backend Attributes: Categorizing products using specific attributes like "wireless connectivity," "speaker type," etc.
By doing this, Amazon ensures its products appear prominently when users search for relevant terms.
Understanding Google Ranking: The Factors That Determine Your Success
Google's goal is simple: to provide the best and most relevant results to its users. To achieve this, Google uses a complex algorithm that evaluates hundreds of ranking factors.
Think of these ranking factors as criteria that Google uses to judge your website. The better you meet these criteria, the higher you'll rank.
- Real Life example: Amazon uses quality content, backlinks,technical SEO, Keyword optimization, user Experience and Schema markup to boost Google Ranking Signals.
Here are some of the most important Google Ranking Signals:
- Quality Content: High-quality, informative, engaging, and relevant content that users find valuable. Google values fresh, unique, and insightful content.
- Backlinks: Links from other reputable websites, signaling trust and authority. A website with many high-quality backlinks is seen as a trusted source of information.
- Technical SEO: A technically sound website that is easy to crawl, index, and understand. Google prioritizes sites that load quickly, are mobile-friendly, and have a clear site structure.
- Keyword Optimization: Using relevant keywords strategically throughout your content to signal what your website is about.
- User Experience (UX): A website that provides a positive user experience. Google wants to show users websites that are easy to navigate, mobile-friendly, and provide a seamless experience.
-
Schema Markup: Structured data markup that helps search engines understand the context of your content.
- Example: Using schema markup to tell Google that a particular section of your page is a recipe, a product review, or a local business listing. This can lead to richer search results and improved visibility.
Important Note: Google's algorithm is constantly evolving. Staying up-to-date with the latest SEO best practices is crucial for maintaining and improving your rankings.
By focusing on these core SEO fundamentals, you can significantly improve your website's visibility in search engines, attract more traffic, and ultimately achieve your business goals.