Skip to main content
Notions of Carvaka philosophy
Charvaka Philosophy
1. Introduction
- Charvaka Darshana (also called Lokayata) is the last of the non-Vedic Darshanas.
- Difficult to reconstruct its tenets due to the lack of surviving literature.
- Knowledge is obtained from fragments in other works.
2. Key Features of Charvaka
-
Materialistic Hedonism: Focuses on material reality and seeking pleasure.
- "Matter is the ultimate reality."
- Rejects divine/transcendental powers behind matter.
- Accepts only what can be perceived.
- Rejects Akasha (ether) as a constituent of reality.
- Rejects Dharma and Moksha as they cannot be seen.
- Accepts only Kama (pleasure) and Artha (wealth) as goals of life.
- Kama is seen as the end of all life.
- Death: The final end of life (no afterlife, no swarga, no naraka).
- Emphasis on direct perception as valid knowledge.
3. Epistemology
- Only valid source of knowledge (pramana) is direct perception (pratyaksha).
- Rejects inference, testimony, and other forms of knowledge.
4. Rejection of Key Entities
- Rejects Akasha (not directly perceivable).
- Rejects Dharma as not directly perceived.
- Rejects Swarga (heaven) as not directly perceived.
- Rejects Ishvara (God) as not directly perceived.
- Rejects Atman (soul) as not directly perceived.
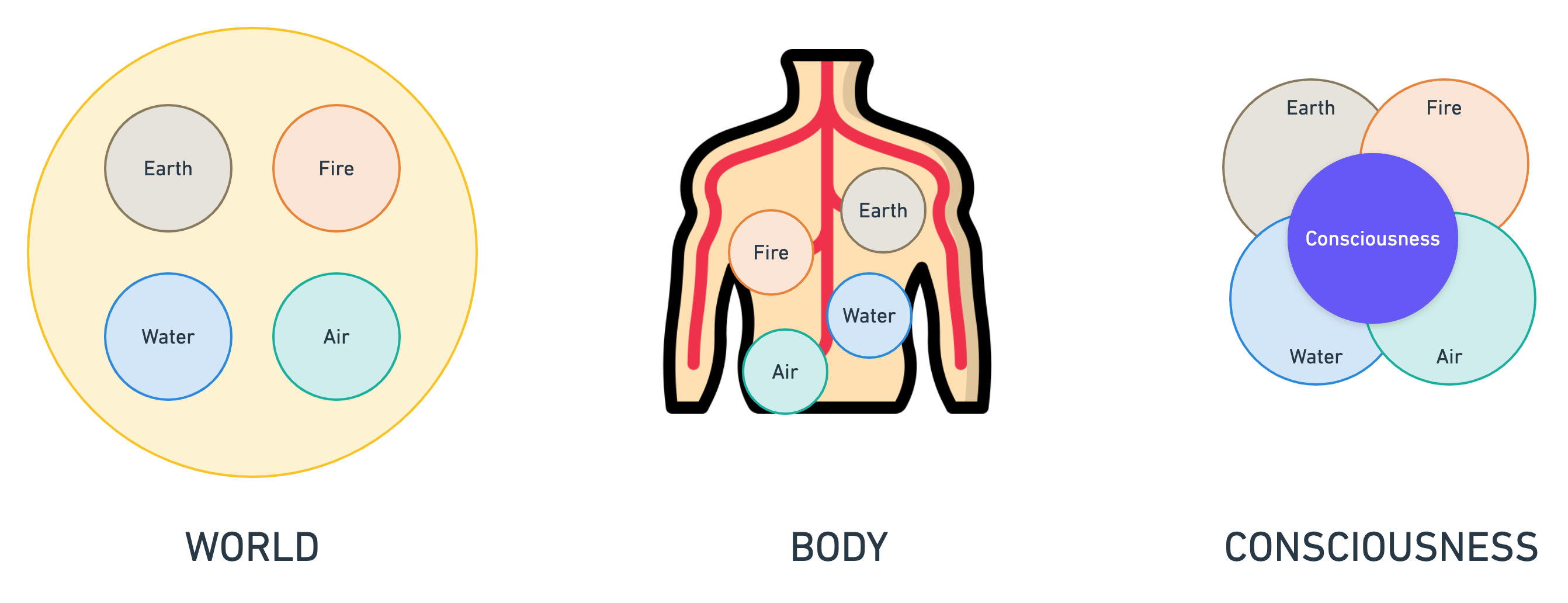
5. Nature of Consciousness
- Consciousness arises from a combination of the four elements.
- Not a separate entity.
- Analogy: Red color in paan (beetle leaf) comes from combining different elements.
- Analogy: Water is the combined properties of Hydrogen and Oxygen.
- Consciousness is a unique combination of earth, fire, water and air elements.
- Consciousness will disappear when that combination breaks.
- No eternal soul/consciousness that transmigrates.
- Consciousness does not go to swarga.
6. Purpose of Life
- Maximize pleasure in one's lifetime.
- Enjoy the present life rather than focusing on some distant future liberation.
7. Summary of Charvaka
- Direct perception is the only source of knowledge.
- Matter is the only reality.
- World composed of four elements.
- Rejection of transcendental entities like god or devas etc..
- Rejection of an afterlife, and also the Atman.
- Consciousness is a product of element combination.
- Goal is to have maximum pleasure in life.
- Does not believe in karma or dharma.

