Tenets of Nyaya School of Philosophy
Nyaya Philosophy: NotesPhilosophy
1. Introduction
- Nyaya is often paired with Vaisheshika due to shared concerns.
- Both analyze experiences (perceptual and non-perceptual).
- Basic Assumption: Valid experience must reflect reality.
- Nyaya believes earlier cognitions must be accepted as real until contradicted.
2. Focus of Nyaya & Vaisheshika
- Nyaya: Focuses on the means of knowing reality.
- Studies how we gain knowledge (e.g., perception, inference).
- Vaisheshika: Focuses on the objects of reality which can be known.
- Studies what can be known, various types of reality.
3. Goal of Knowledge
- The right knowledge of both the means of knowing and what can be known leads to liberation.
- All Vedic schools aim at liberation or ultimate happiness.
4. Key Figure and Development
- Gautama Rishi is the founding figure ( Nyaya Sutras).
- Around 14th century, Gangesopadhyaya shifted the focus more on pramanas (means of knowledge).
- This led to the "Navya Nyaya" (New Nyaya) which focuses on detailed inquiry into knowledge.
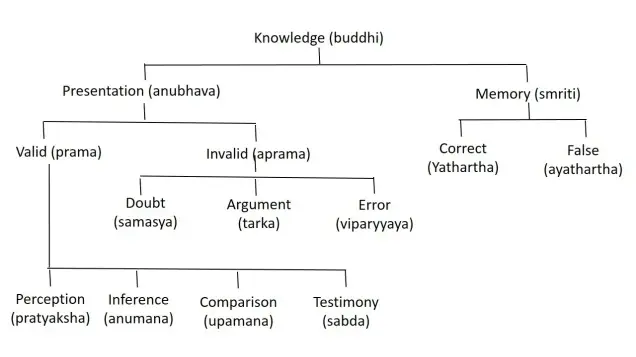
5. Core Questions of Navya Nyaya
- What is knowledge?
- What are the various means of acquiring knowledge?
- How is right knowledge different from false cognition, dream or doubt?
- What are the means to cognize an objective?
- Systematic way to arrive at true conclusions, hypothesis to conclusions.
6. Methodology and Epistemic Concepts
- Nyaya created rules for debating, which became widely accepted standards.
- Other traditions have also engaged with their methodology & epistemology.
7. Concept of Liberation
- Liberation (moksha): Cessation of all pain and suffering.
- It is not a positive state of infinite happiness, but the absence of pain and suffering.
8. Concept of Ishvara
- Accepts Ishvara as the creator but not as the creator out of nothing.
- Paramanu (atoms): infinite, eternal are material cause.
- Ishvara: Efficient cause.
- Ishvara has a unique role in the following:
- Author of the Vedas (making them infallible).
- Directs karma (the karmic law) and dictates the next life based on present actions.