Skip to main content
Unique features of Indian philosophical systems
Unique Features of Indian Philosophical Systems
I. Transmission and Development of Ideas
-
Guru-Shishya Parampara: Philosophical ideas were primarily transmitted through a Guru-shishya parampara (teacher-student lineage)
-
Oral Dialogue: Philosophical learning was mainly through oral discussions with the help of texts.
-
Textual Framework: The development involved:
-
Sutra texts: Foundational texts
-
Bhashyas: Commentaries on Sutras
-
Varthikas: Explanatory texts and textbooks.
II. Unique Characteristics of Indian Philosophy
A. Intertwining with Religion
-
Integration: Philosophy in India is closely intertwined with religion and religious thought, unlike other traditions.
-
Philosophical Ideas in Religious Texts: Philosophical ideas are embedded within religious texts such as the Ramayana, Mahabharata, and the Bhagavad Gita.
-
Lack of Sharp Distinction: In pre-modern India, there was no sharp distinction between philosophy and religion.
-
Dialectic Relationship: There was a give-and-take or dialectic relationship between philosophy and religion.
- Philosophy provided the theoretical basis for addressing existential issues
- Religion provided the operational principles for mundane life.
- Religious practices were often seen as necessary to achieve spiritual goals.
- Religion provided a discipline to achieve ultimate knowledge/happiness.
B. Shared Concepts
-
Karma: All traditions believed in Karma and its consequences.
- Good and bad actions create consequences which must be borne in this or future lives.
-
Transmigration (Samsara): Belief in rebirth, based on accumulated karma and the cycle of birth and death (samsara chakram).
-
Free Will: Belief that while some things are determined by past karma, there is an element of free will that allows individuals to choose their actions in the present.
-
Moksha: All systems aim to achieve moksha (liberation) from the cycle of birth and death and achieve ultimate happiness through right knowledge and action.
C. Common Parameters
- All Darshanas agreed on the need for achieving Moksha as the ultimate goal.
-
Ontology and Epistemology: All systems had clearly defined concepts relating to ontology (the nature of being) and epistemology (the study of knowledge)
-
Rigorous Methodologies: They developed rigorous methodologies to define and understand:
* The concepts needed to attain moksha
* The nature of cognition, knowledge, and the difference between them.
* The nature of Ishvara (divine)
-
Healthy Culture of Debating:
- Different schools had disagreements.
- A healthy culture of debate was practiced, in order to reconcile different views.
- The debates were not derogatory but were used for mutual learning.
- This ethic was carried on by both the thinkers and their followers.
V. Classification of Indian Philosophical Systems
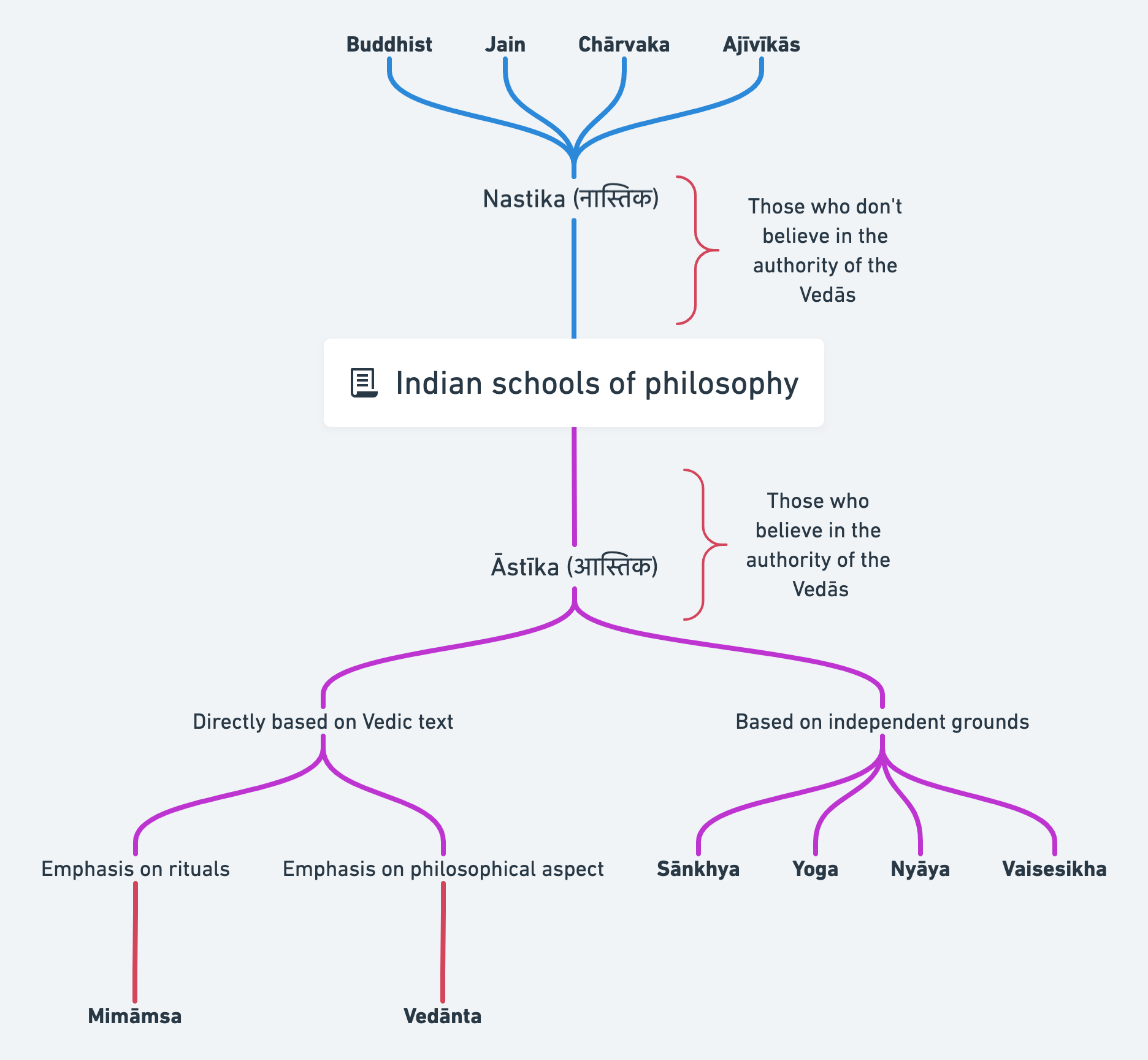
A. Broad Classification
-
Vedic (Astika): Those that accept the authority or testimony of the Vedas.
-
Non-Vedic (Nastika): Those that do not accept the authority or testimony of the Vedas.
B. Important Note
- This classification based on acceptance of Vedas has no connection with their belief in God.
- Both Astika and Nastika traditions may or may not have a belief in God.
C. Astika Systems
- Those who accept the authority of the Vedas
-
Six Major Schools:
* Samkhya
* Yoga
* Nyaya
* Vaisesika
* Mimamsa
* Vedanta
D. Nastika Systems
- Those who do not accept the authority of the Vedas.
-
Three Major Systems:
E. Clarification
- The Mimamsa system (Astika) does not believe in Ishvara, while Jaina and Buddhism (Nastika) have their own conceptions of God and heaven.
- Popular connotations of astika and nastika are different from the classifications used for Indian philosophical traditions.
VI. Conclusion
- The Indian philosophical systems developed their own concepts of Jiva, Jagat and Ishvara.
- Each system has its own focus area within the broad context.

