Augmented Reality
Virtual Reality (VR)
- Definition: A computer-generated representation of another universe or reality, often experienced through 3D movies, virtual tours, and video games.
- Usage: Beyond gaming and entertainment, VR is applied in training, education, and science to create immersive simulations.
- How It Works: VR simulates vision using a headset that blocks the real world, with graphics rendered via an HDMI cable connected to a PC or mobile. It employs goggles, speakers, and wearables for a full sensory experience, including visual, audio, and haptic feedback.
Augmented Reality (AR)
- Definition: A technology blending digital elements with the real world, enhancing physical environments with digital content.
- Usage: AR is used in applications like score overlays on live sports, and 3D images in physical spaces.
- How It Works: Utilizing computer vision, mapping, and depth tracking, AR overlays digital content onto the real world as viewed through devices like smartphones.
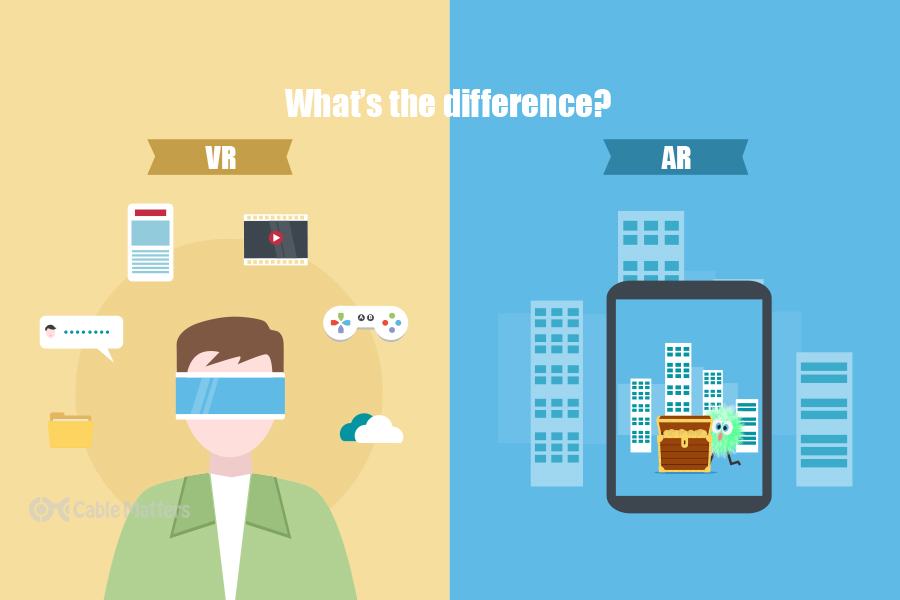
Difference between AR and VR
| Feature | Virtual Reality (VR) | Augmented Reality (AR) |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Entirely immersive virtual environment | Enhances real scene with digital elements |
| Sensory Control | Controls the visual senses | Keeps user aware of the real environment |
| Reality Composition | 75% virtual, 25% real | 25% virtual, 75% real |
| Bandwidth Requirement | At least 50 Mbps for full immersion | Up to 100 Mbps for partial immersion |
| Hardware | Requires VR headset | No headset required |
| User Interaction with Reality | Isolated from real world | Interacts with virtual items in the real world |
| Application | Primarily gaming and fictional realities | Enhances both real and virtual worlds |
| Level of Immersion | Complete cutoff from outside world | Enhances physical world without isolation |
VR's Goal: To create completely immersive fictional experiences.
AR's Goal: To augment the real world with digital enhancements for practical applications, such as turning a windshield into a head-up display for driving.
Both technologies aim to enhance user experiences but differ significantly in application and user interaction with the real world.
