Competitive Dymanics
Competitive Dynamics
Competitive Strategies for Market Leaders
- Expand total market demand: Find new users or increase usage among existing users.
- Protect market share: Defend against competitors' attacks.
- Increase market share: Gain a larger slice of the market.
CompetitiveMarket Challenger Strategies
for
What Is a Market ChallengersChallenger?
A market challenger is a company or brand that holds the second, third, or another significant position in the market and seeks to challenge the market leader to gain a larger market share. Unlike the market leader, challengers are aggressive in their tactics and aim to disrupt the leader's dominance.
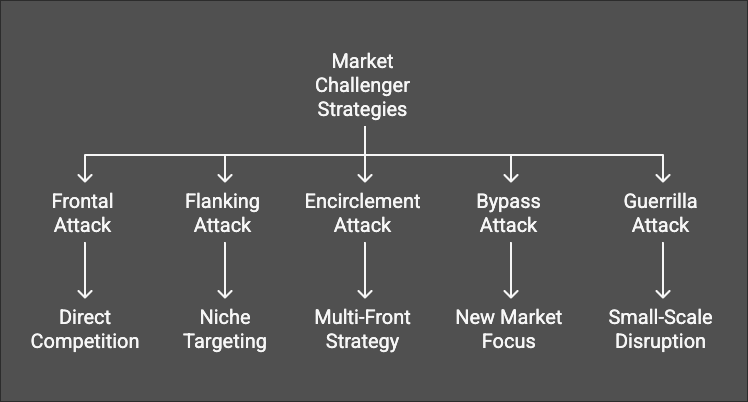
Five Main Market Challenger Strategies
1. Frontal Attack
-
FrontalDefinition:attack:The challenger directly targets the competitor (often the market leader) by matching or exceeding their strengths. -
Approach:
- Compete head-on in terms of price, product quality, distribution, or marketing.
- Requires significant resources to compete on equal footing.
- Risks: High risk if the market leader retaliates or if the challenger lacks sufficient resources.
- Example: PepsiCo directly competing with Coca-Cola by offering similar pricing, advertising campaigns, and distribution strategies.
2. Flanking Attack
-
Definition: The challenger identifies and targets weak areas
Directlyorchallengeunderserved segments of the market leader. -
Approach:
- Focus on niches or geographic regions ignored by the leader.
- Innovate in areas where the leader's offerings are weak.
- Risks: Requires precise market research to find gaps; can be costly to establish a presence in new segments.
- Example: Tesla disrupted traditional automakers by focusing on the underserved electric vehicle (EV) market when it was still a niche.
3. Encirclement Attack
- Definition: The challenger uses a comprehensive strategy to attack the leader on multiple fronts, such as price, product features, or customer service.
-
Approach:
- Launch multiple products or variations to meet different customer needs.
- Overwhelm the competitor by addressing their strengths and weaknesses simultaneously.
- Risks: Resource-intensive strategy requiring large investments in R&D and marketing.
- Example: Samsung competing with Apple by releasing smartphones at various price points and offering diverse features.
4. Bypass Attack
- Definition: The challenger avoids direct competition with the market leader and instead focuses on new markets, technologies, or distribution channels.
-
Approach:
- Enter new or unrelated markets where the leader is not present.
- Develop innovative products or technologies.
- Risks: May involve high initial investment and uncertainty about the success of new markets or technologies.
- Example: Amazon bypassed traditional bookstores by focusing on online retail and digital books with its Kindle devices.
5. Guerrilla Attack
- Definition: The challenger uses small, intermittent attacks to weaken the market leader without provoking a significant response.
-
Approach:
- Launch targeted promotional campaigns or price cuts in specific regions or segments.
- Employ unconventional tactics like viral marketing or flash sales.
- Risks: Results may be short-term if not part of a broader strategy.
- Example: Local businesses using flash sales or social media marketing to disrupt larger competitors in a specific region.
Key Factors for a Successful Market Challenger Strategy
- Resource Strength: The challenger must evaluate its financial and operational resources compared to the leader.
-
FlankMarketattack:Research: Understanding the competitor's weaknesses and customer needs is critical for choosing the right strategy. - Innovation: Differentiating products or services through innovation can provide a significant edge.
-
Customer Focus:
onBuilding loyalty by meeting underserved or unmet customer needs helps gain market share.
Summary Table: Market Challenger Strategies
| Strategy | Definition | Risks | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal Attack | Directly competes with the leader in price, quality, or distribution. | High retaliation risk and resource dependency. | Pepsi vs. Coca-Cola. |
| Flanking Attack | Targets the leader's |
Requires precise market research. | Tesla in the EV market. |
| Encirclement |
Attacks on multiple |
Resource-intensive and high-cost. | Samsung vs. Apple. |
| Bypass |
Avoids |
High investment and uncertainty in new markets. | Amazon (Kindle). |
| Guerrilla |
Small, |
Results
|
Local businesses using flash sales. |
Conclusion
Market challenger strategies allow businesses to grow their market share and compete effectively with leaders. The choice of strategy depends on the challenger’s resources, market conditions, and the leader’s weaknesses. Each strategy comes with risks but can yield significant rewards if executed properly.
Market Follower Strategies for(4 Types)
What Is a Market FollowersFollower?
A market follower is a company that imitates the products, services, or strategies of market leaders without trying to become the market leader itself. These companies typically aim to maintain a stable position in the market without directly challenging the leader’s dominance.
4 Types of Market Follower Strategies
1. Imitation
-
Counterfeiter:Definition:DuplicateA market follower replicates the leader's productandorsellserviceitwith minimal changes, typically at a lowerprice.cost. -
Cloner:Approach:Copy- Offers similar products with minor improvements or modifications.
- Focuses on keeping prices competitive to appeal to price-sensitive customers.
- Risks: Product imitation can result in legal or patent issues. There is also a lack of differentiation in the market.
- Example: Many smartphone manufacturers (e.g., Xiaomi) imitate Apple or Samsung's designs, often offering similar features at lower prices.
2. Cloning
- Definition: A market follower creates an almost identical product or service to that of the leader.
-
Approach:
- Close reproduction of the leader's offerings, both in terms of features and branding.
- Often involves large-scale production to reduce unit costs and offer a competitive price.
- Risks: Potential for legal issues regarding intellectual property or patents, and the product may be seen as lacking originality.
- Example: Generic pharmaceutical companies that produce "generic" versions of branded medications.
3. Adapting
-
Definition: The follower makes adjustments to the leader's product
withorslightservicemodifications.to better fit local or niche markets. -
Imitator:Approach:Copy- Modify
aspectsproducts or services for specific regional, cultural, or consumer preferences. - Often involves minor adjustments in design, packaging, or features to cater to local tastes.
some - Modify
- Risks: The changes may fail to meet the expectations of the target market, and the process of adaptation may be costly.
- Example: McDonald's adapts its menu items in different countries (e.g., offering the "McAloo Tikki" in India).
4. Counterfeiting
- Definition: The follower produces a copy of the leader’s product but with little or no variation.
-
Approach:
- Products are almost identical to the leader’s, and the follower focuses on creating a similar brand image.
- This is a high-risk strategy, often associated with illegal or unethical practices, and leads to intellectual property infringement.
- Risks: Legal consequences, brand reputation issues, and customer dissatisfaction if the counterfeit product is of poor quality.
- Example: Counterfeit fashion products that copy the designs of high-end brands like Gucci or Louis Vuitton.
Market Follower Strategy Summary Table
| Strategy | Definition | Risks | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Imitation | Replicates the leader’s product with minimal changes. | Limited differentiation, legal risks. | Xiaomi imitating Apple or Samsung phones. |
| Cloning | Creates an almost identical product or service to the leader’s offering. | Legal issues, lack of originality. | Generic pharmaceuticals. |
| Adapting | Modifies the leader's product |
Adaptation may not always succeed. | McDonald's adapting menu globally. |
| Counterfeiting | Produces a nearly identical product, often with poor quality. | Legal and ethical risks, poor quality. | Counterfeit luxury goods. |
Market Nicher Strategy
What Is a Market Nicher?
A Adapter:market nicher Improvefocuses on the leader's product and offertargeting a betterspecific version.segment of the market that is often overlooked by larger competitors. The strategy involves offering specialized products or services that cater to the unique needs of a small but profitable customer group.
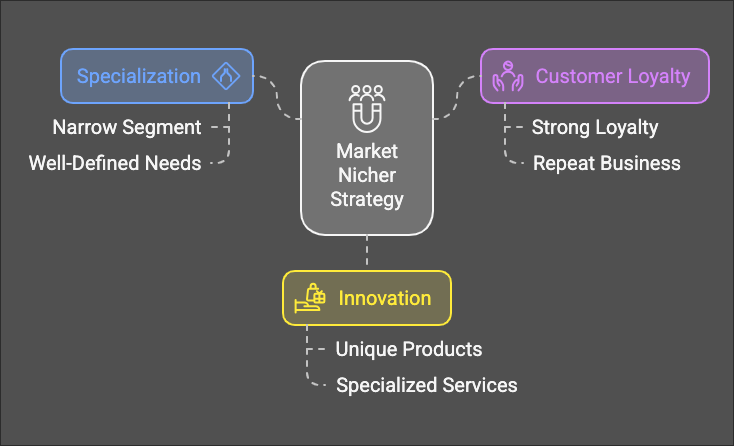
CompetitiveKey StrategiesFeatures forof Market NichersNicher Strategies
-
FocusSpecialization: Market nichers focus on aspecificnarrowcustomerandsegment:well-definedSpecialize in serving a niche market.segment. -
DevelopCustomeruniqueLoyalty:expertise:ByBecomefocusingtheonexpertnicheinmarkets,anichersparticularcanarea.build strong customer loyalty. -
BuildInnovation:strongNicherscustomeroftenrelationships:differentiateCultivatethemselvesloyaltybyamongofferingnicheuniquecustomers.or specialized products that appeal to a select group.
Examples of Market Nicher Strategies:
-
Targeting Niche Demographics: Catering to specific age groups, lifestyles, or other customer segments.
- Example: Specialized clothing brands for plus-size women (e.g., Lane Bryant).
-
Offering Specialized Products: Offering unique products that appeal to specific needs.
- Example: High-end audio equipment for audiophiles (e.g., Bang & Olufsen).
-
Serving Underserved Geographies: Providing products or services in locations where competitors are absent or underserved.
- Example: Providing organic food products in smaller, rural markets.
-
Creating a Unique Customer Experience: Providing a unique value proposition that competitors cannot easily replicate.
- Example: Boutique hotels offering personalized luxury experiences.
Advantages of Market Nicher Strategy:
- Less Competition: Niche markets often have fewer direct competitors, allowing nichers to dominate the space.
- Higher Profit Margins: By offering specialized products or services, market nichers can often charge higher prices and achieve better profit margins.
- Stronger Customer Loyalty: Niche markets tend to have a loyal customer base due to the personalized nature of the products or services.
Risks of Market Nicher Strategy:
- Limited Market Size: By focusing on a small segment, market nichers may experience limited growth.
- Vulnerability to Changes: Nichers are often vulnerable to changes in consumer preferences or economic downturns.
- Dependence on a Single Segment: Over-reliance on one niche can be risky if market conditions change.
Market Nicher Strategy Summary Table
| Strategy | Definition | Examples | Risks/Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Niche Demographics | Focus on specific demographic groups (age, gender, etc.). | Specialized clothing, products for seniors. | Small market size, limited growth. |
| Specialized Products | Offer unique products targeting a specific need. | Audiophile equipment, custom motorcycles. | May face market saturation over time. |
| Underserved Geographies | Serve locations with minimal competition. | Organic food in rural areas. | Geographical limitations. |
| Unique Customer Experience | Provide personalized services or products. | Boutique hotels, custom-made jewelry. | Dependence on customer loyalty. |
Conclusion
- Market Follower Strategies are about strategically mimicking or adjusting the leader’s offerings, focusing on cost advantages, efficiency, and responsiveness.
- Market Nicher Strategies focus on specialization and catering to unique customer needs, providing high customer loyalty and often higher margins, albeit with some risks.
Both strategies offer unique paths to success depending on market conditions and the company’s capabilities.