New Product Development
New Product Development
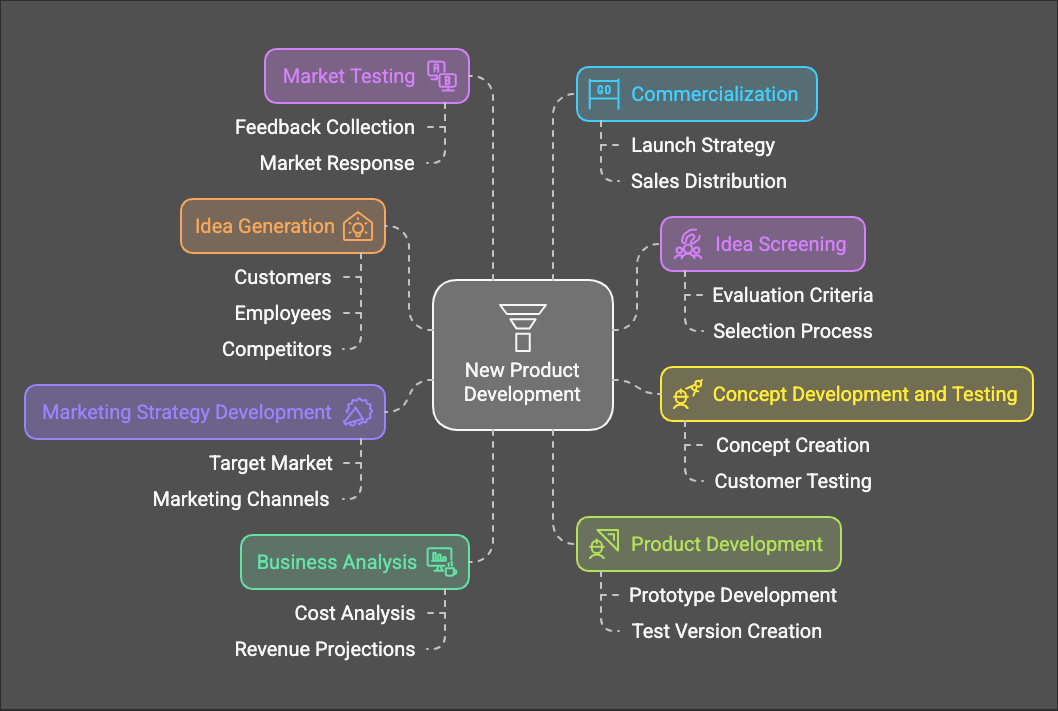
Stages of New Product Development
Bringing a new product to life is a journey with several stages:
- Idea Generation: Coming up with new product ideas from various sources (customers, employees, competitors, etc.).
- Idea Screening: Evaluating ideas and selecting the most promising ones.
- Concept Development and Testing: Creating a detailed concept and testing it with potential customers.
- Marketing Strategy Development: Developing a plan to market the new product.
- Business Analysis: Evaluating the financial viability of the new product.
- Product Development: Creating a prototype or a test version of the product.
- Market Testing: Introducing the product in a limited market to gather feedback.
- Product Launch: Launching the product to the full market.
Categories of New Products
- New-to-the-world products: Completely new inventions that create a whole new market.
- New product lines: Products that allow a company to enter an existing market for the first time.
- Additions to existing product lines: New products that supplement a company's existing product lines.
- Improvements and revisions of existing products: Making existing products better.
- Repositioned products: Existing products targeted at new markets or segments.
- Cost reductions: New products that provide similar performance at a lower price.
Reasons for Launching New Products & Causes of Failure
According to Philip Kotler's "Marketing Management," launching new products is vital for a company's growth and survival. However, it's also a risky endeavor. Let's explore the reasons for launching new products and the common causes of failure, drawing insights from Kotler's work.
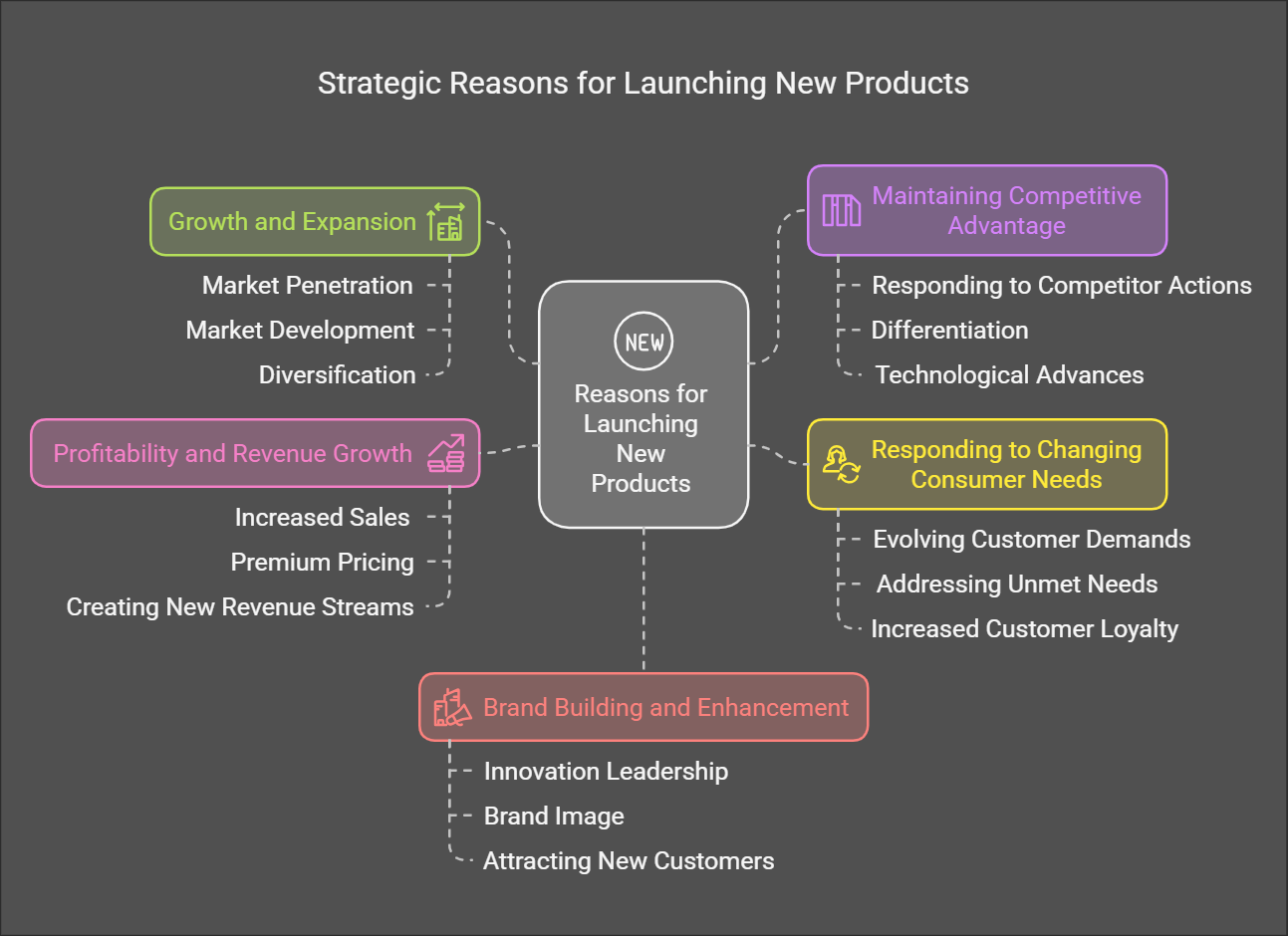
Reasons for Launching New Products
Kotler emphasizes that continuous innovation is crucial for a company to remain competitive and relevant in the market. Here are the main reasons companies launch new products:
-
Growth and Expansion:
- Market Penetration: New products can help a company capture a larger share of an existing market. This can be achieved by offering variations of existing products or by targeting new customer segments within that market. (Kotler discusses market penetration strategies extensively).
- Market Development: New products can enable a company to enter entirely new markets or geographic regions. (Kotler discusses market expansion via market development).
- Diversification: New products can allow a company to move into entirely new industries, reducing reliance on a single market. (Kotler emphasizes diversification as a growth strategy.)
-
Maintaining Competitive Advantage:
- Responding to Competitor Actions: When competitors launch new products, a company needs to respond to maintain its position or lose market share. (Kotler discusses competitive strategies in detail).
- Differentiation: New products can differentiate a company from its rivals, making it more appealing to consumers. (Kotler highlights the importance of differentiation and positioning).
- Technological Advances: Companies may launch new products to capitalize on emerging technologies and offer cutting-edge solutions. (Kotler stresses the importance of innovation and staying abreast of technological trends).
-
Responding to Changing Consumer Needs and Preferences:
- Evolving Customer Demands: As consumer preferences shift, companies must innovate to meet those changes and ensure continued relevance. (Kotler discusses the importance of understanding consumer behavior and market research.)
- Addressing unmet needs: New products can fulfill needs that haven't been adequately addressed by existing products or services.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: Successfully launching products that meet the changing needs of their consumers can increase customer loyalty and brand advocacy.
-
Profitability and Revenue Growth:
- Increased Sales: New products, especially successful ones, contribute directly to revenue growth and profitability.
- Premium Pricing: Innovative or high-quality new products may allow a company to command a higher price point, improving profit margins.
- Creating New Revenue Streams: Diversifying product offerings allows companies to create multiple revenue streams reducing reliance on the existing product line.
-
Brand Building and Enhancement:
- Innovation Leadership: Launching new products positions a company as innovative and forward-thinking, attracting customers who value such qualities.
- Brand Image: Successfully launching products that are relevant to the changing landscape builds a strong brand image.
- Attracting New Customers: Successful new products can bring in new customers who may be attracted to the new offerings.
Reasons for New Product Failure
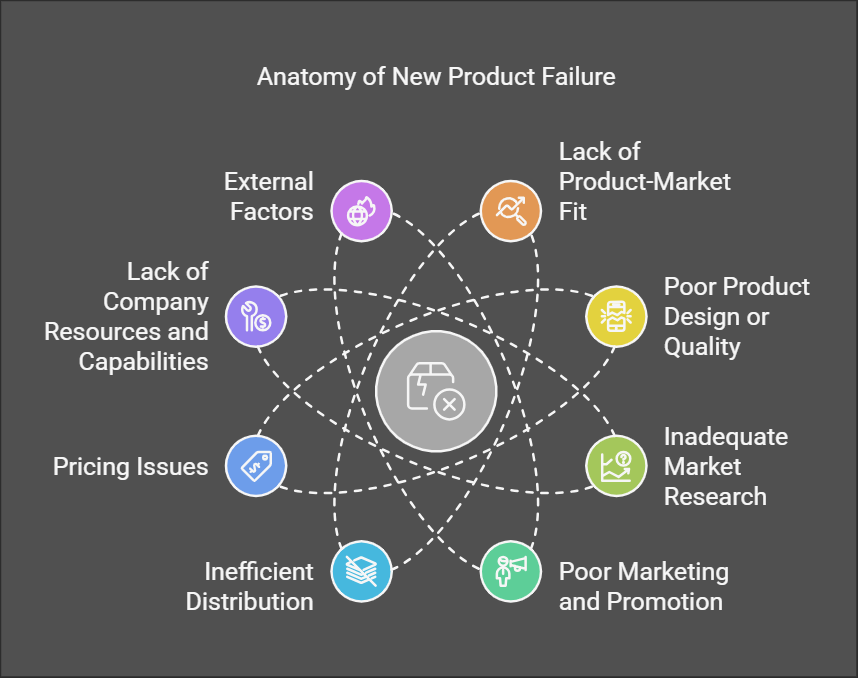
Despite the potential rewards, many new products fail. Kotler outlines several reasons why:
-
Lack of Product-Market Fit:
- Misunderstanding Customer Needs: The product doesn't solve a genuine customer problem or address a real need. (Kotler underscores the need for thorough market research and understanding customer needs.)
- Poor Value Proposition: The product doesn't offer sufficient benefits compared to existing alternatives or is overpriced. (Kotler discusses the importance of crafting a strong value proposition).
- Incorrect Targeting: The product is not targeted at the right customer segment.
-
Poor Product Design or Quality:
- Technical Flaws: The product doesn't function as intended or has significant flaws or quality issues.
- Poor User Experience: The product is difficult to use or lacks essential features that enhance user experience.
- Lack of Thorough Testing: Insufficient testing and quality assurance during product development.
-
Inadequate Market Research:
- Insufficient Market Analysis: Companies may launch products based on assumptions rather than data, or they may misunderstand the competitive landscape.
- Failing to Assess Demand: Launching products that lack sufficient market demand or those that are not relevant. (Kotler stresses the need for proper market research to understand demand, competition, etc.)
-
Poor Marketing and Promotion:
- Ineffective Communication: The value proposition is not clearly communicated to the target market.
- Insufficient Budget: The company doesn't invest enough resources in marketing and promotion to generate awareness and sales.
- Incorrect Marketing Channels: The product is not promoted through the right channels to reach target audiences.
-
Inefficient Distribution:
- Limited Availability: If customers can't find the product, they can't buy it.
- Poor Logistics: Issues with supply chain, distribution, or transportation can lead to customer dissatisfaction.
-
Pricing Issues:
- Too Expensive: The price is too high for the value offered, deterring potential customers.
- Too Low: The price may be too low to generate sufficient profit or may convey a perception of low quality. (Kotler emphasizes the need for strategic pricing decisions).
-
Lack of Company Resources and Capabilities:
- Insufficient Expertise: Companies may not have the required expertise to develop, market, or distribute the product effectively.
- Inadequate Financial Support: The company doesn't allocate enough financial resources to support product development and launch.
-
External Factors:
- Changes in the Economy: Economic downturns or shifts in consumer spending can impact the success of a new product.
- Technological Changes: Technological advancements can make products obsolete or less appealing.
- Competitive Actions: Aggressive moves by competitors can hinder the success of a new product.