What is Consumer Marketing Channels ?
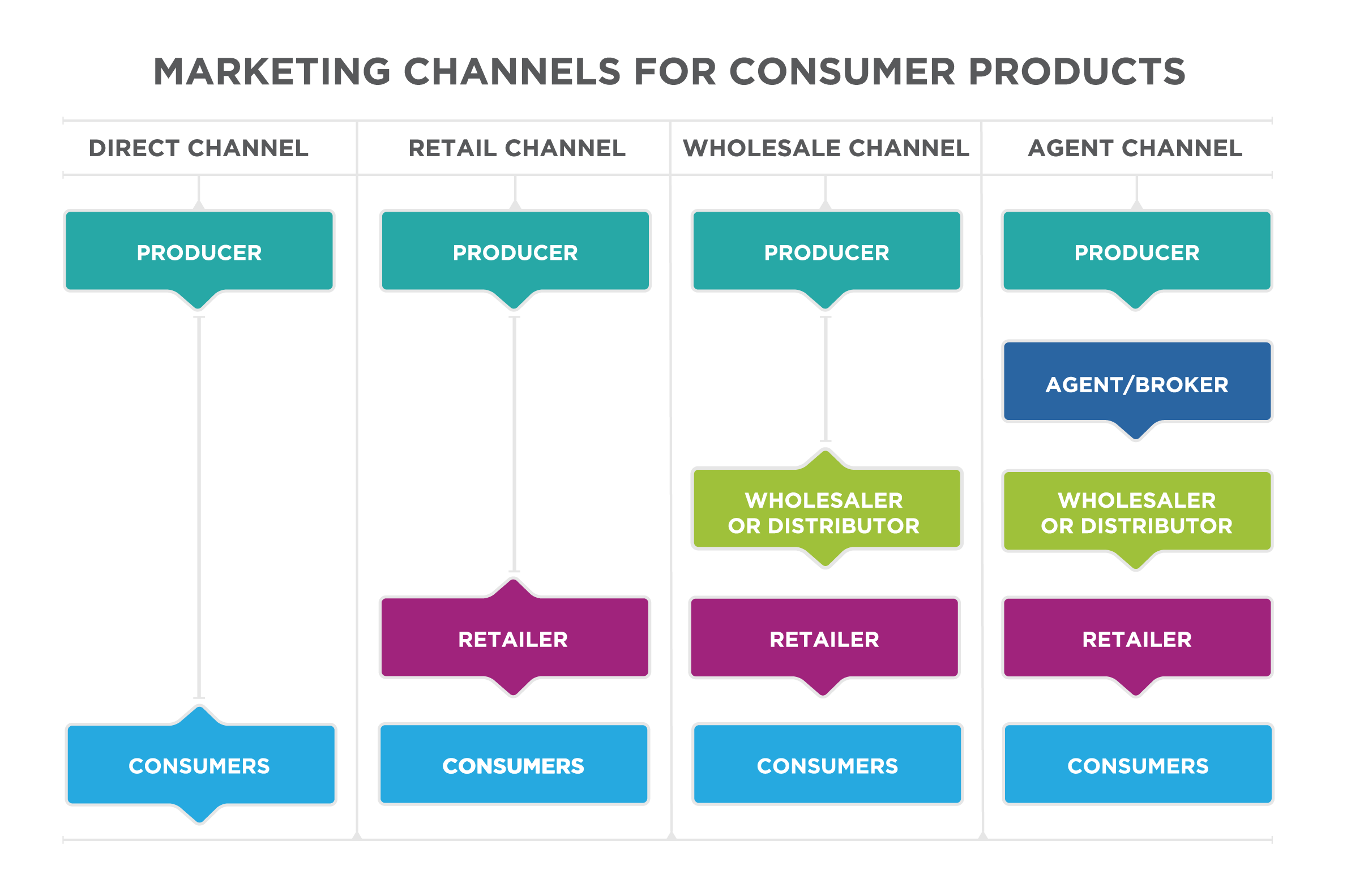
Consumer Marketing Channels
- 0-level: Manufacturer to Consumer
- 1-level: Manufacturer to Retailer to Consumer
- 2-level: Manufacturer to Wholesaler to Retailer to Consumer
- 3-level: Manufacturer to Wholesaler to Jobber to Retailer to Consumer
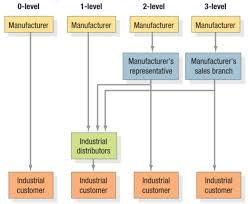
Industrial Marketing Channels
- 0-level: Manufacturer to Industrial Customer
- 1-level: Manufacturer to Industrial Distributors to Industrial Customer
- 2-level: Manufacturer to Manufacturer's Representative to Industrial Distributors to Industrial Customer OR Manufacturer to Manufacturer's Sales Branch to Industrial Customer
- 3-level: Manufacturer to Manufacturer's Sales Branch to Industrial Distributors to Industrial Customer
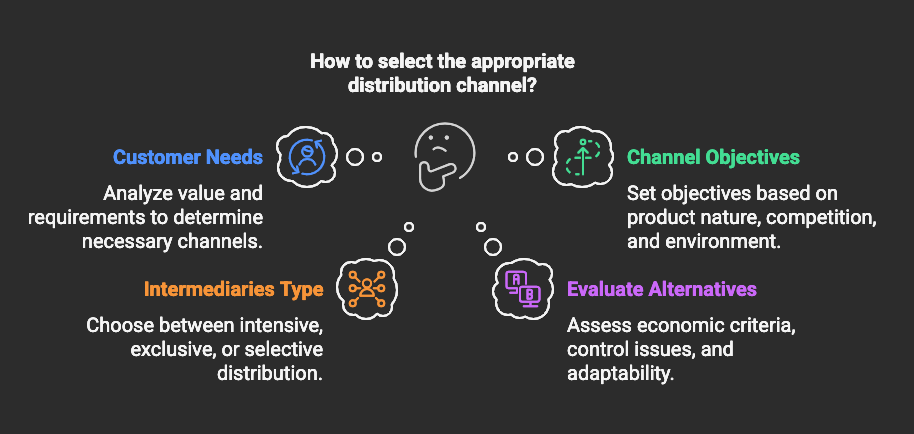
Criteria for Selecting a Channel
1. Analyzing Customer Needs
- Value provided to the customer by each delivery network.
- Studying customer requirements and the need for more channels.
2. Setting Channel Objectives
- Identifying segments requiring different service levels and the best channels for them.
- Considering the nature of products (e.g., perishable goods require avoiding delays).
- Considering competitors (e.g., competing in the same area to facilitate comparison shopping).
- Environmental factors like economic conditions.
3. Identifying Major Alternatives
Type of Intermediaries: Selecting the specific type of intermediaries required.
- Finalizing the degree of channels required.
- Example: Dell's shift from D2C to multi-channel distribution.
- Using multi-channels to reach more customers (though they may target the same customer).
*Number of Marketing Intermediaries: - Intensive Distribution: Stocking products in as many outlets as possible (e.g., convenience products).
- Exclusive Distribution: Giving a limited number of dealers the exclusive right to distribute the company's products in their territories (e.g., luxury brands).
- Selective Distribution: Using more than one, but fewer than all, intermediaries willing to carry the company's products (e.g., furniture brands, jewelry).
4. Evaluating Major Alternatives
- Economic Criteria: Comparing costs, expected sales, and profitability of different channel alternatives.
- Control Issues: Determining the level of control that needs to be given to the channels. The company aims to have as much control as possible.
- Adaptability Criteria: Ensuring new channel development doesn't negatively impact the profitability of existing channels, as channels involve long-term commitments.