Skip to main content
What is Physical Distribution
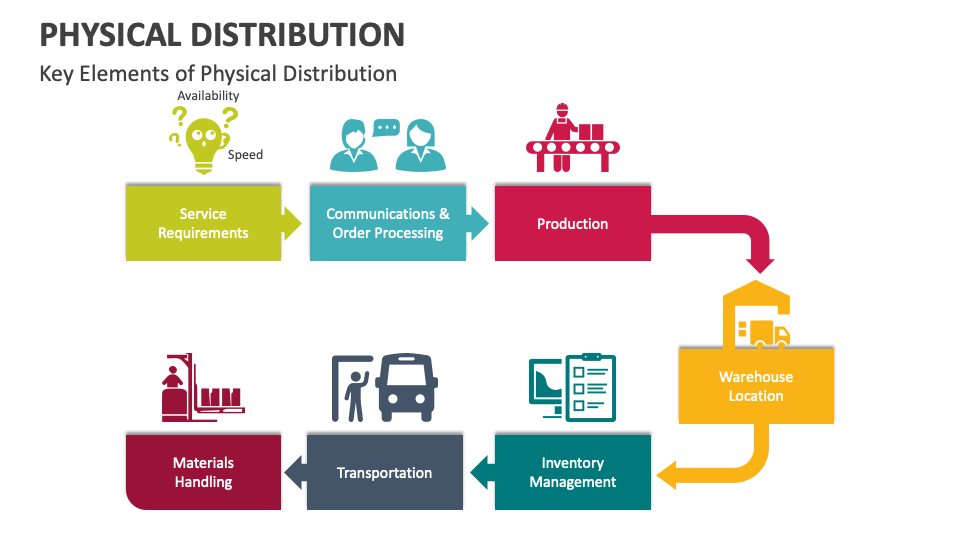
Physical Distribution (Marketing Logistics)
-
Marketing Logistics: Planning, implementing, and controlling the physical flow of materials, final goods, and related information from points of origin to points of consumption to meet customer requirements at a profit.
-
Supply Chain Management: Managing upstream, downstream, and reverse value-added flows of materials, final goods, and related information among suppliers, the company, resellers, and final consumers.
[Image of Logistics management]
Importance of Logistics
- Improved logistics provides better service or lower prices to customers.
* - Competition is centered around delivery and logistics.
* - Good logistics results in high cost savings.
* - IT and automation improvements lead to efficient distribution. (e.g., software POS scanners, RFID tags, satellite tracking).
* - The need for smarter logistics management arises from the huge variety of products being shipped.
* - Sustainable supply chains are necessary due to the carbon footprint of transportation, warehousing, and packaging.
Major Logistics Functions
-
Warehousing:
- Storage warehouses store goods for moderate to long periods.
- Distribution centers are highly automated warehouses designed for efficient order fulfillment and delivery.
-
Inventory Management:
- Maintaining the right quantity of inventory is crucial.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) logistics systems are used to reduce costs.
-
Transportation:
- Carrier choices affect product pricing.
- Modes include trucks, rail, water, pipeline, and air.
- The Internet is a mode for digital products.
- Many companies use multi-modal transportation.
-
Logistics Information Management:
*
- Information sharing is done through Electronic Data Interchange (EDI).
- Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) systems are used for product replenishment.
Integrated Logistics Management
- Emphasizes teamwork within the company and among channel partners to maximize distribution system performance.
-
Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Provider: An independent provider that performs any or all functions to get a client's product to market.

