Mutual Funds Structure
Mutual funds involve several key participants, each playing a distinct role in their creation, operation, and regulation. Here's a breakdown of the major players:
1.
Financial SponsorsAsset Management Structure
Depository
Asset Management Company
Fund Sponsor
Trustees
Agent
Custodian
Financial Asset Management Structure
Depository
Fund Sponsor
Asset Management Company
Trustees
Agent
Custodian
Mutual Fund Structure
Depository
Asset Management Company
Fund Sponsor
Trustees
Agent
Custodian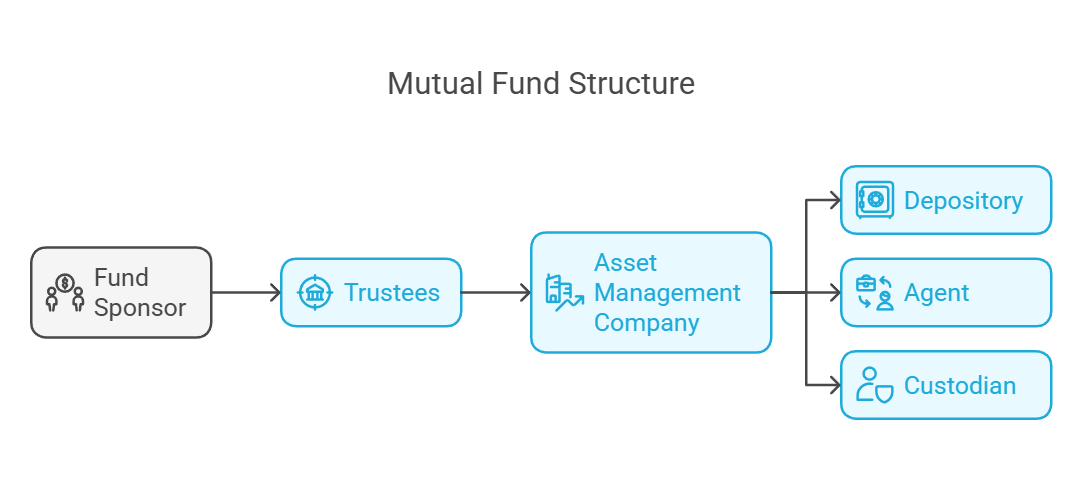
-
Definition:Rectangles:The sponsor isRepresent theentityprimarythatentitiesinitiatesinvolved:theFundestablishmentSponsor,ofTrustees,aandmutualAssetfund.ManagementThey are akin to the promoters of a company.Company. -
Role:Rounded Rectangles: Represent the service providers: Depository, Agent, and Custodian. - Arrows: Indicate the flow of responsibility and relationships.
Participants and Their Roles
-
Fund Sponsor:
ConceptualizesRepresentedandbysetsauprectangle on the far left, indicating its role as the initiator of the mutual fund.AppointsSymbolized by an icon of people and money, signifying its role in bringing together investors' capital.-
Role: The entity that conceives the
initial trustees and the Asset Management Company (AMC). Contributes at least 40%idea of thenetmutualworthfund,ofestablishes theAMC.fund, Registersandtheregistersmutual fundit with the regulatoryauthorityauthorities.(e.g.,It'sSEBIanalogousintoIndia).the promoter of a company.
-
Eligibility (Example: In India, as per SEBI):Trustees:SoundRepresentedtrackbyrecordaand general reputation for fairness and integrity in financial dealings.At least five years of experiencerectangle in thefinancialmiddle,servicesconnectedindustry.to the Fund Sponsor by an arrow.PositiveSymbolizednetbyworthanforicon of a building with pillars and a target, representing stability, oversight, and thepreceding five years.Profits after depreciation, interest, and tax in at least threeprotection oftheunitholderimmediately preceding five years, including the latest year.
Example:A large financial institution or a corporate entity with a strong financial background can be a sponsor.Definition:Trustees are the guardians of the mutual fund's assets and are responsible for protecting the interests of the unit holders.interests.-
Role:
- Appointed
Holdby thepropertyFundofSponsor, themutualtrusteesfundhold the fund's assets in trust for the benefit of theunitunitholdersholders.(investors). OverseeThey are responsible for overseeing theactivitiesoperations of theAMCfund,toensuringensureitcomplianceacts in accordance withregulationsthe trust deed, regulations, and thescheme'sbestobjectives.interests Approveof theappointment of key personnel, auditors, and custodians.Monitor the fund's performance and ensure transparency.Enter into an Investment Management Agreement with the AMC.investors.
-
Structure:Can be a board of trustees (individuals) or a trustee company.In India, at least two-thirds of the trustees must be independent (not associated with the sponsors).
Responsibilities:Ensure the fund is managed according to the trust deed and regulations.Review transactions, net worth, and performance of the AMC.Approve new schemes and ensure proper disclosure.Safeguard the interests of the unit holders.
- Represented by a rectangle to the right of the Trustees, connected by an arrow.
- Symbolized by an icon of a building with a graph, indicating its role in managing investments and growing the fund's assets.
-
Definition:Role:TheAppointed by the Trustees, the AMC is responsible formanagingtheinvestmentsday-to-day management of themutualfund'sfund.investments.ItThisisincludes making investment decisions (buying and selling securities), conducting research, and administering the fund's operations. -
Depository:
- Represented by a
companyroundedapprovedrectangle on the far right, connected to the AMC by an arrow. - Symbolized by an icon of a safe, representing the
regulatorysecureauthoritystorage(e.g.,ofSEBI in India).securities. -
Role:
ManagesHolds theday-to-dayfund'soperationssecuritiesofinthe mutual fund.Makes investment decisionsdematerialized (buyselectronic) form, ensuring their safekeeping andsellsfacilitatingsecurities)electronicon behalf of the fund.Conducts research and analysis to identify investment opportunities.Floats new schemes (after approval from trustees and regulators).Ensures compliance with investment objectives and restrictions.Calculates and declares the Net Asset Value (NAV).transactions.
-
Appointment:Agent:Appointed- Represented by
theasponsorroundedorrectangle below thetrustees.AMC, connected by an arrow. - Symbolized by an icon of people and a briefcase, representing the intermediary role between the fund and investors.
-
EligibilityRole:(Example: In India,Acts asperaSEBI):distributor- or
Soundbroker,track record and experience in financial services.Minimum net worth requirement.Board of directors with at least 50% independent directors.Key personnel with relevant experience and no record of misconduct.
4. CustodianDefinition:The custodian is responsible for the safekeeping ofselling the mutual fund'sassetsunits(securities).to investors. They may also provide investment advice to investors.
- Represented by
-
Custodian:
- Represented by a rounded rectangle below the Agent, connected by an arrow.
- Symbolized by an icon of a person, representing the entity responsible for safeguarding the fund's assets.
-
Role:
- Holds
the securities (shares, bonds, etc.) owned by the mutual fund. Ensuresthe physicalor dematerialized safekeeping of assets.Collects dividends, interest, and other income on behalfcustody of thefund.fund's Settlesassets (securities), ensuring their safekeeping and managing related transactions (deliverye.g.,ofcollectingsecuritiesdividends,whensettlingsold, receipt of securities when purchased)trades).
- Holds
- Represented by a
2. Trustees
3. Asset Management Company (AMC)
:
Flow Appointedof byResponsibility
The arrows in the trustees.diagram illustrate the flow of responsibility:
- The Fund Sponsor initiates the fund and appoints the Trustees.
- The
Independence:TrusteesIn many jurisdictions (including India),appoint thecustodianAMCmusttobemanageindependentthe investments. - The AMC utilizes the services of the
sponsorDepository, Agent, and Custodian toavoidcarryconflictsoutofitsinterest.functions effectively.
5.Conclusion
The Agentsimage (Registrarprovides a clear and Transferconcise Agentsvisual - R&T Agents)
Definition:Transfer agents maintain the records of unit holders.Role:Process applications, redemptions, and transfers of units.Maintain records of unit holder transactions (purchases, sales, switches).Issue account statements and other communications to unit holders.Handle dividend payouts and other corporate actions.
Appointment:Appointed by the AMC.
6. Unit Holders
Definition:The investors who purchase unitsrepresentation of the mutual fundschemes.structure. - It
Rights:Beneficial ownership ofhighlights theassetskeyofparticipantsthe–schemeFundinSponsor,proportionTrustees,toAMC, Depository, Agent, and Custodian – and theirholdings.respective Receive dividends (if declared under the dividend option).Participateroles in thegrowthestablishment,of the fund's NAV (under the growth option).Right to informationmanagement, anddisclosures about the fund's performance and operations.Right to vote on certain matters (e.g., winding up of a scheme).
7. Auditors
Role:Conduct independent audits of the mutual fund's financial statements.Verify compliance with accounting standards and regulations.Provide an audit report to the trustees, which is included in the annual report.
Appointment:Appointed by the trustees.
8. Regulatory Body (e.g., SEBI in India)
Definition:The regulatory authority that oversees the functioning of mutual funds in a particular jurisdiction.Role:Frame regulations and guidelines for theoperationof mutual funds.Register and approve mutual funds, AMCs, and other participants.Monitor compliance with regulations.Conduct inspections and investigations.Protect the interests of investors.Take enforcement actions against violations.Promote the development of the mutual fund industry.
9. Distributors/Brokers/Advisors
Role:Distribute mutual fund schemes to investors.Provide investment advice (in the case of advisors).Earn commissions on the sale of mutual fund units (in regular plans).
Types:BanksIndependent Financial Advisors (IFAs)Brokerage firmsOnline platforms
10. Other Service Providers
Legal Advisors:Provide legal counsel to the mutual fund, trustees, and AMC.Fund Accountants:Maintain the accounting recordsof the fund.- The
ComplianceflowchartOfficers:formatEnsureeffectivelythatdemonstrates theAMCflow of responsibility and thefund comply with regulations.
Interrelationships
The participantsinterconnectedness of athese mutualentities fundin are interconnected and work together to ensureensuring the smooth functioning of the fund. Here's a simplified view of their relationships:
Sponsorsinitiate the mutual fundandappoint theTrusteesand theAMC.Trusteesoversee theAMCand appoint theCustodianandAuditors.AMCmanages the fund's investments, appointsTransfer Agents, and works withDistributorsto market the schemes.Unit Holdersinvest in the fund and benefit from the services of all other participants.TheRegulatory Bodyoversees the entire ecosystem, ensuring compliance and protectinginvestorinterests.protection
Conclusion
The various participants inwithin a mutual fund structure play crucial roles in ensuring its proper functioning, transparency, and investor protection. Understanding these roles and their interrelationships is essential for investors to make informed decisions and for the overall health of the mutual fund industry.fund.
