Concept of Production and Production System
Concept of Production
What is Production?
Production is the process of transforming inputs into outputs. It's broader than just manufacturing, which focuses on tangible goods. Production encompasses both tangible goods (like cars) and intangible services (like healthcare).
Three Perspectives on Production:
- Production as a System: This is the focus of the diagram. It views production as an interconnected set of processes with inputs, transformations, outputs, and feedback.
- Production as an Organizational Function: This perspective looks at production as a key function within an organization, alongside marketing, finance, etc.
- Decision Making in Production: This emphasizes the various decisions involved in managing production, from strategic long-term choices to daily operational decisions.
The Production System Model:
The diagram illustrates the production system as a flow:
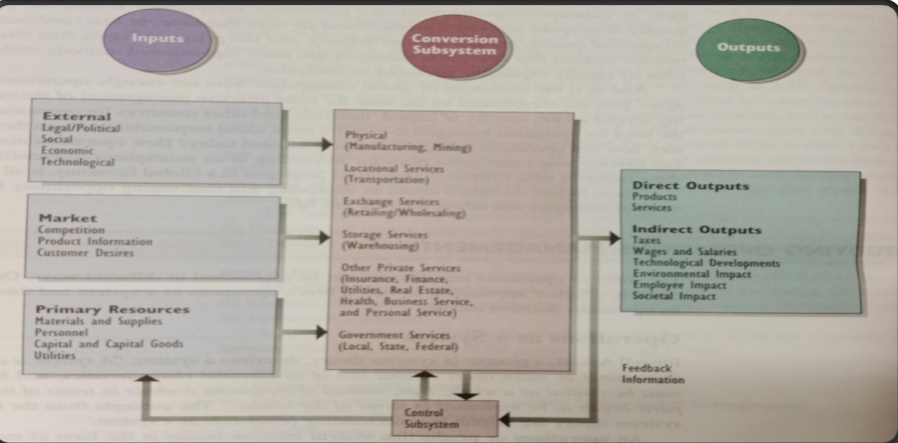
-
Inputs: Resources that enter the system. These can be categorized as:
- External Inputs: Information about the external environment (legal, political, social, economic, technological).
- Market Inputs: Information about the market (competition, product information, customer desires).
- Primary Inputs: Resources directly used in production (materials, personnel, capital, utilities).
- Conversion Subsystem: The core of the system where inputs are transformed into outputs. This includes various processes like manufacturing, transportation, and service delivery.
-
Outputs: The results of the production process. These can be:
- Direct Outputs: The intended products or services.
- Indirect Outputs: Byproducts of the production process, including taxes, wages, environmental impact, and societal impact.
- Control Subsystem: Monitors outputs and provides feedback to ensure the system is functioning effectively. This involves measuring quality, cost, and quantity, and making adjustments as needed.
Decision Making in Production:
Effective production management requires making informed decisions at different levels:
- Strategic Decisions: Long-term decisions about products, processes, and facilities. These shape the overall direction of production.
- Operating Decisions: Short-term decisions about production planning and scheduling to meet demand.
- Control Decisions: Day-to-day decisions to ensure smooth operations and maintain quality standards.
