Scope of Production and Operations Management
Scope of Production and Operations Management
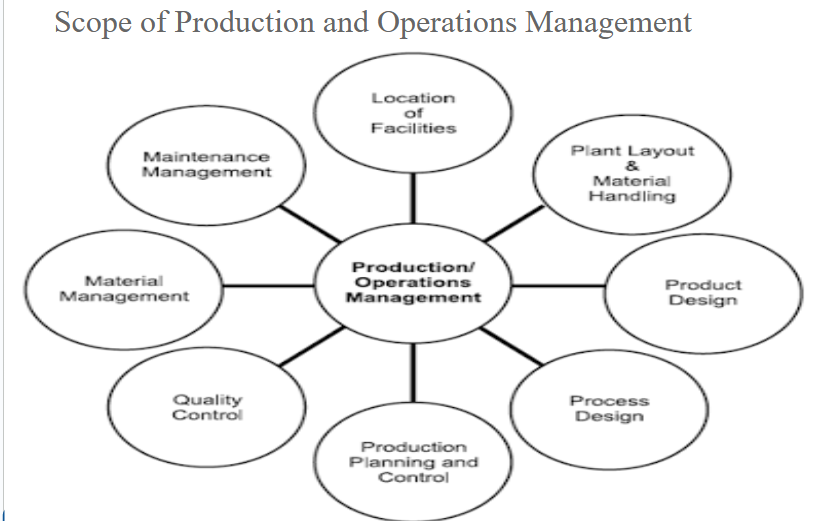
Production and operations management encompasses a wide range of activities crucial for efficiently and effectively producing goods or services. Here's a breakdown of the key areas:
1. Location of Facilities Management:
- Strategic Decision: Selecting the right location for production facilities is a critical long-term decision.
-
Factors to Consider:
- Proximity to markets and raw materials
- Availability of skilled labor
- Transportation costs
- Infrastructure (utilities, roads, etc.)
- Legal and regulatory environment
- Potential for future expansion
2. Plant Layout and Material Handling:
- Efficient Design: Optimizing the arrangement of facilities, equipment, and workspaces within a plant to ensure smooth workflow and minimize material handling costs.
-
Objectives:
- Increase output and productivity
- Improve product quality
- Reduce production costs
- Enhance worker safety and satisfaction
3. Product Design:
- Competitive Advantage: Developing innovative and well-designed products is essential for success in today's market.
-
Key Considerations:
- Functionality and usability
- Aesthetics and appeal
- Cost-effectiveness
- Quality and durability
- Environmental impact
4. Process Design:
- Selecting the Right Process: Determining the most efficient and effective production process for a given product.
- Workflow Analysis: Analyzing the flow of work and identifying areas for improvement.
-
Tools and Techniques:
- Flowcharts
- Process simulation software
- Scale models
5. Production Planning and Control:
- Coordinating Production: Planning and controlling production activities to meet demand and achieve production targets.
-
Key Activities:
- Planning: Determining what, how much, when, and how to produce.
- Routing: Selecting the path for raw materials to be processed.
- Scheduling: Setting the timing for each production activity.
- Dispatching: Authorizing and initiating production activities.
6. Quality Control:
- Maintaining Standards: Implementing systems to ensure that products meet or exceed quality standards.
-
Objectives:
- Customer satisfaction
- Cost reduction through defect minimization
- Brand image and reputation
7. Materials Management:
- Efficient Procurement: Acquiring, controlling, and utilizing materials efficiently.
-
Objectives:
- Minimize material costs
- Optimize purchasing, transportation, and storage
- Develop strong supplier relationships
8. Maintenance Management:
- Keeping Operations Running: Maintaining equipment and machinery to ensure smooth and uninterrupted production.
-
Objectives:
- Minimize downtime and maximize equipment availability
- Reduce maintenance costs
- Ensure worker safety