Prakriti and Its Evolution: Understanding the Nature of the Individual
Introduction
Here we explore the concept of Prakriti (nature) and its evolution in Indian psychology, providing a framework for understanding the nature of the individual.
Prakriti and Its Evolution
Prakriti, in the context of Sankhya philosophy, refers to the primordial substance from which the entire universe evolves. This evolution occurs through a series of transformations, starting with Mahat (cosmic intelligence), followed by Ahankara (ego), and then the five subtle elements (tanmatras) and the five gross elements (panchabutas). These elements combine to form the physical world and the individual's body.
The Human Being: A Holistic View
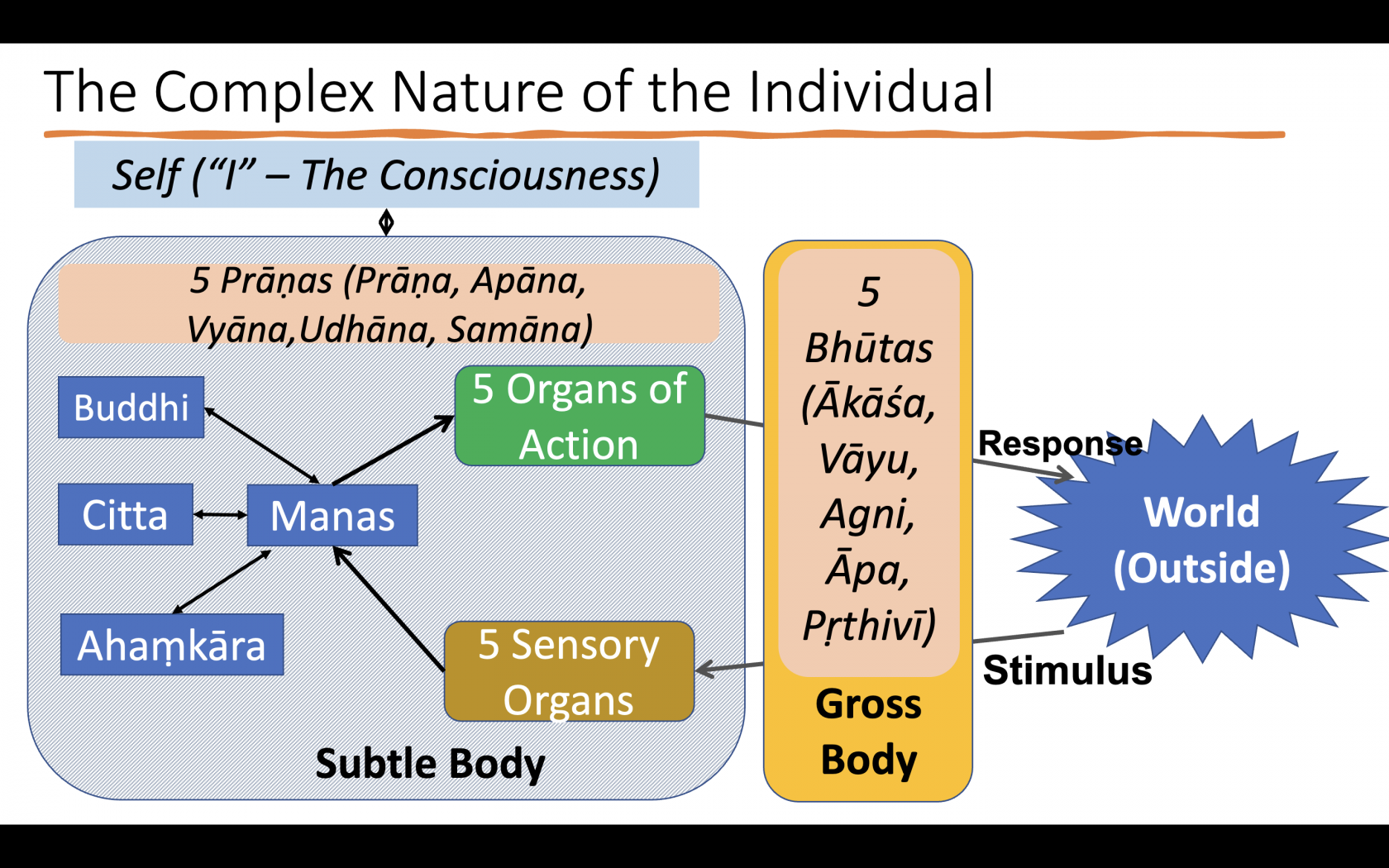
Indian psychology views the human being as a complex interplay of both physical and non-physical elements. The physical body is composed of the five gross elements, while the non-physical aspects include the senses, mind (manas), intellect (buddhi), ego (ahankara), and consciousness (purusha).
The Role of the Self
The self, or consciousness, is considered the witness to all experiences and actions. It is the true nature of the individual, distinct from the ever-changing mind and body.
A Holistic Picture of the Individual
Indian psychology emphasizes a holistic picture of the individual, taking into account both the gross body and the subtle body. The gross body is composed of the five gross elements, while the subtle body consists of the senses, mind, intellect, ego, and the pranas (vital energies). The self, or consciousness, is the ultimate reality, and all activities of cognition and action occur for the self.
Conclusion
Understanding Prakriti and its evolution provides a framework for understanding the nature of the individual in Indian psychology. This holistic approach, considering both physical and non-physical aspects, offers a comprehensive understanding of human experience.