6. The Four Influences Framework
- Four
AInfluences Framework in International Human Resource Management (IHRM)The Four Influences Framework is a conceptual model used in International Human Resource Management (IHRM) to analyze the various factors that influence HRM practices in multinational corporations (MNCs). This framework recognizes that
highlightsIHRMtheiskeynotfactorsainfluencingstandaloneIHRM:function but is shaped by a complex interplay of various forces. Understanding these influences is crucial for developing effective IHRM strategies and policies.The four primary influences are:
- Organizational Factors
- Host-Country Factors
- Home-Country Factors
- Global Factors
Let's explore each of
Originthese(HostinCountry):detail:1. Organizational Factors
Organizational factors are internal to the MNC and significantly impact IHRM practices. These include:
-
Company Strategy:
-
Example:Global Strategy:AMNCsUS-basedwithcompanyaoperatingglobalinstrategyChinaseekwillto standardize products and services across all locations, leading to centralized HR practices. There might beinfluencedabystrongChinesepushlaborforlaws,globalculturaltalentnorms,management andeconomicuniformconditions.policies. - Multidomestic Strategy: MNCs with a multidomestic strategy adapt products and services to local market needs, requiring more decentralized and localized HR practices. This involves greater autonomy for local HR managers.
- Transnational Strategy: MNCs with a transnational strategy seek a balance between global integration and local responsiveness, necessitating a more sophisticated IHRM approach that can manage both standardization and localization.
-
-
CountryOrganizationalof Origin (Parent Country):Structure:-
Example:Centralized Structure:TheDecision-makingparentiscompany'sconcentratedvalues,atculture,headquarters, leading to more standardized and globally consistent HRpracticespolicies.willThisinfluencemighthowinvolveitmoreoperatesexpatriateinassignmentsotherforcountries.controlAandUS-basedcoordination. - Decentralized Structure: Decision-making is delegated to local subsidiaries, leading to more localized and context-specific HR policies. Local HR managers have more autonomy to adapt practices.
-
Matrix Structure: In a matrix structure, employees may
prioritizereportcertaintomanagementmultiplestylesmanagers,orcreatingemployeecomplexbenefitsreportingthatlinesareandcommonrequiringinIHRMthetoUS.manage cross-functional teams effectively.
company -
-
CountryOrganizationalof Third Country Nationals (TCNs):Culture:-
Example:Strong Culture:IfAn organization with aUSstrong and unified culture might seek to export that culture to its foreign subsidiaries through HR practices. This can influence recruitment, training, and performance management. - Weak Culture: Organizations with weak or diverse internal cultures may have more flexibility in adapting HR practices to local contexts.
-
-
Size and Age of the MNC:
- Large, Mature MNCs: Often have more formalized and sophisticated HR systems, well-defined IHRM processes, and more resources for international assignments.
- Small, Younger MNCs: May have less formalized HR practices and less experience with IHRM, facing unique challenges in managing international operations.
-
Technology:
- Advanced technology can streamline HR processes like recruitment, communication, and performance management across different locations.
- The use of HRIS (Human Resource Information Systems) allows MNCs to maintain better data and manage globally dispersed workforces.
2. Host-Country Factors
Host-country factors are external influences that originate from the country where the MNC operates its subsidiaries. These include:
-
Legal and Regulatory Environment:
- Labor Laws: Variations in labor laws regarding working hours, minimum wages, termination policies, and employee rights significantly influence HRM practices.
- Immigration Laws: Rules and regulations governing work permits and visas impact the hiring of expatriates and foreign workers.
- Data Privacy Laws: Laws related to the collection, storage, and use of employee data vary across countries, affecting HR data management.
- Equal Opportunity and Anti-Discrimination Laws: Variations in anti-discrimination laws influence recruitment, selection, and promotion processes.
-
Economic Conditions:
- Labor Market Dynamics: Scarcity or surplus of labor, skills gaps, and unemployment rates affect recruitment strategies, compensation, and training investments.
- Cost of Living: Significant differences in the cost of living between the home country and the host country impact compensation and benefits packages.
- Economic Development: Developing countries may have different HRM needs and challenges compared to developed countries.
-
Political Stability and Risk:
- Political instability and corruption in a host country can pose significant challenges for IHRM, requiring careful risk assessment and contingency planning.
-
Cultural Norms and Values:
- Individualism vs. Collectivism: Influences team dynamics, performance management, and reward systems.
- Power Distance: Impacts leadership styles, communication, and organizational hierarchy.
- Uncertainty Avoidance: Affects the level of structure and formality in the workplace.
- Masculinity vs. Femininity: Influences compensation, work-life balance, and competition within the organization.
-
Education and Skills Levels:
- The availability of a skilled workforce in the host country can significantly impact recruitment, training, and development strategies.
-
Industrial Relations Systems:
- The influence of labor unions, collective bargaining agreements, and dispute resolution mechanisms in the host country shape employee relations.
3. Home-Country Factors
Home-country factors are influences that originate from the MNC's country of origin. These include:
-
Legal and Regulatory Environment:
- Home-country labor laws may impact how MNCs manage their operations abroad, particularly concerning the treatment of employees from their home country.
-
Cultural Values and Norms:
- The MNC's home-country culture influences organizational culture, management styles, and HRM practices implemented abroad.
- Ethnocentric approaches may involve exporting home-country practices to foreign subsidiaries, sometimes leading to cultural clashes.
-
Economic Conditions:
- Economic conditions in the home country can affect the investment decisions and overall strategy of the MNC.
-
Management Philosophy:
- The leadership values and philosophies of the parent company
hiresinfluence the IHRM strategies adopted in the foreign subsidiaries.
- The leadership values and philosophies of the parent company
4. Global Factors
Global factors are external influences that operate at a
Britishmacroemployeelevel and impact IHRM across different countries. These include:-
Globalization:
- Increasing interconnectedness of countries through trade, investment, and technology impacts the global mobility of talent and requires HR to
workmanage diverse workforces. - Globalization increases the competitive pressures on MNCs, leading them to focus on talent acquisition and retention strategies.
- Increasing interconnectedness of countries through trade, investment, and technology impacts the global mobility of talent and requires HR to
-
Technological Advancements:
- Technological innovations in
China, the British employee's cultural backgroundcommunication andexpectationsdatawillmanagementinfluencehave revolutionized IHRM processes. - Remote work and virtual teams have become increasingly common, requiring IHRM to adapt to new ways of managing global teams.
- Technological innovations in
-
Political and Economic Instability:
- Global events, such as economic recessions, pandemics, or political conflicts, impact MNCs operations and require them to adapt their
workIHRMexperiencestrategiesandtoperformance.handle crisis situations.
- Global events, such as economic recessions, pandemics, or political conflicts, impact MNCs operations and require them to adapt their
-
International
Influences:Organizations and Agreements:- Agreements and guidelines from international organizations (e.g., ILO, WTO) can influence labor practices and regulations globally.
-
Global Talent Mobility:
- The increased movement of skilled workers across borders influences talent acquisition strategies for MNCs.
- Competition for top talent is now global, requiring IHRM to develop innovative and competitive compensation and benefits packages.
-
Global Ethical Standards:
- Increasing attention on corporate social responsibility and ethical practices influences how MNCs manage their global operations, requiring adherence to international labor standards and human rights.
Implications of the Framework:
The Four Influences Framework helps IHRM professionals:
-
Examples:Understand the complexity of global HR:Globalization,Ittechnologicalhighlightsadvancements,that IHRM is not just about people management but also about navigating a complex set of internal and external influences. - Develop context-specific strategies: By considering all four influences, IHRM strategies can be tailored to fit the unique circumstances of each MNC and its operations in different countries.
- Identify potential challenges: The framework helps anticipate challenges arising from cultural differences, legal variations, and economic conditions.
- Optimize HR practices: By understanding the interplay of these influences, IHRM can develop HR practices that are effective, efficient, and culturally appropriate.
-
Make strategic decisions: The framework supports better decision-making regarding global talent management, international
tradeassignments,agreements,and strategic planning.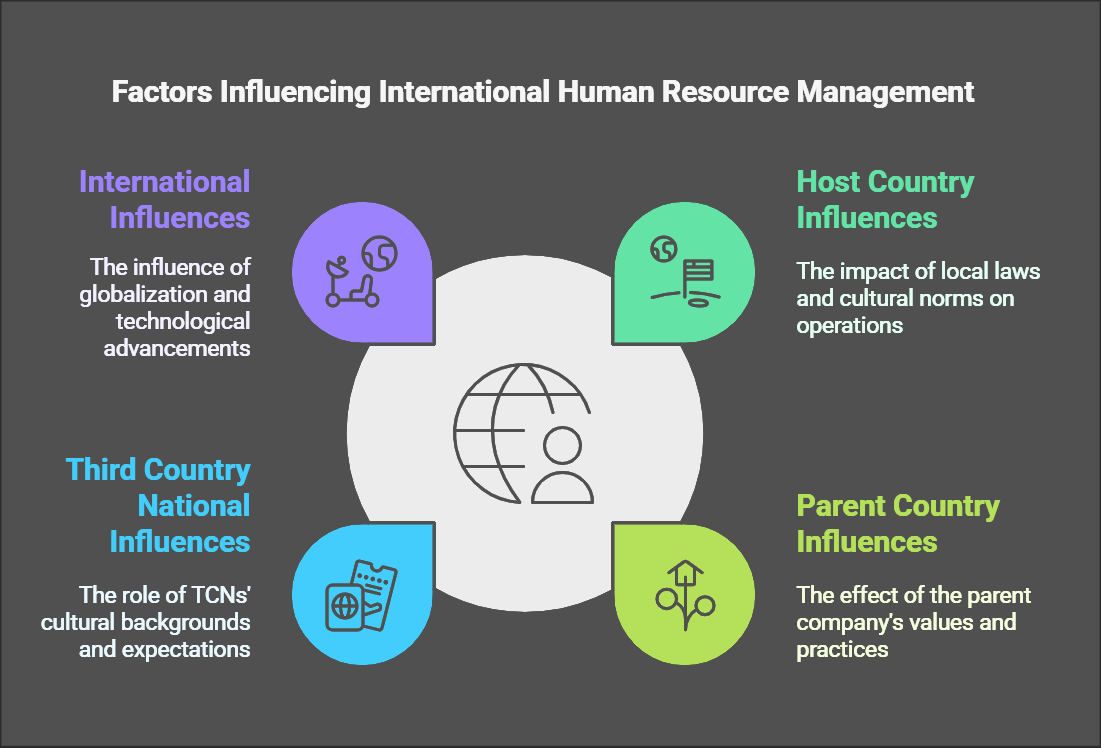 Conclusion:
Conclusion:
The Four Influences Framework serves as a valuable tool for IHRM practitioners by providing a comprehensive approach to analyze and understand the factors that shape HR practices in multinational corporations. By considering the organizational, host-country, home-country, and global
competitioninfluences,allIHRMshapeprofessionals can develop strategies and policies that are tailored to specific contexts, thereby enhancing thecontexteffectiveness ofIHRM.global
