The Buyer Decision Process and Business buyer decision process
The Buyer Decision Process in Marketing
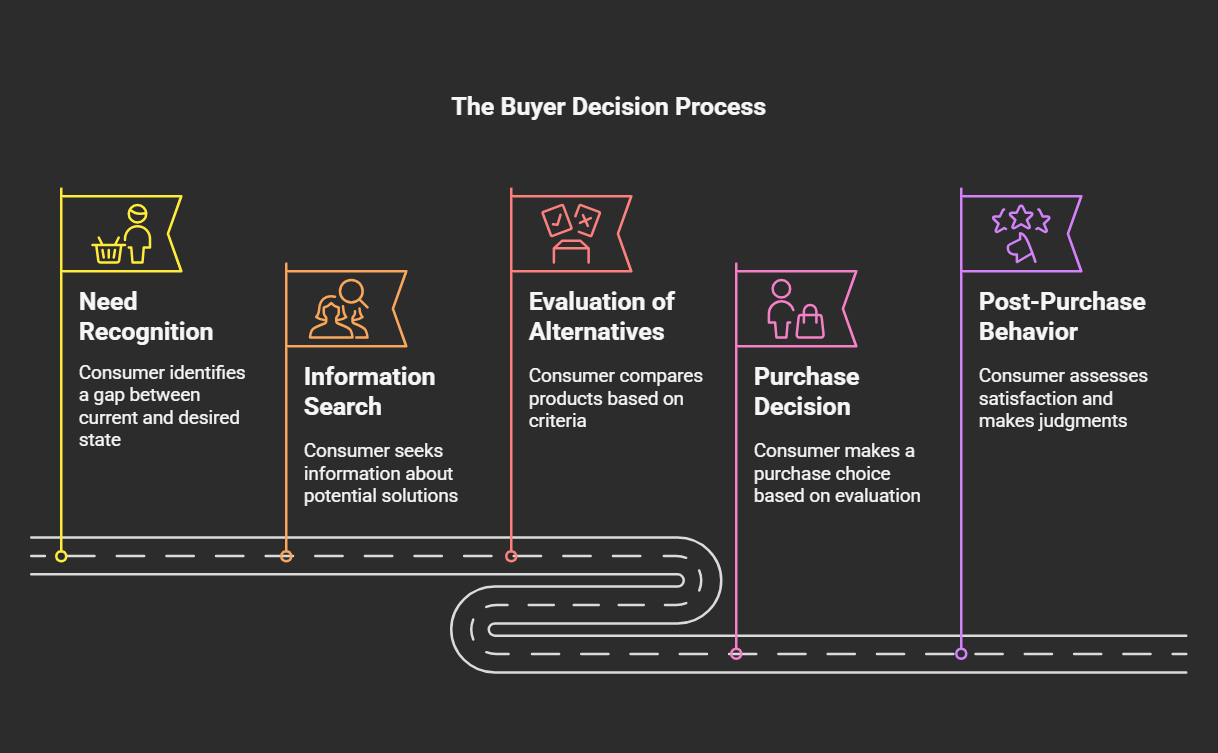
The buyer decision process is a fundamental concept in marketing, outlining the steps a consumer goes through when deciding to make a purchase. Understanding this process allows marketers to target their efforts more effectively. Here's a breakdown of the five stages:
1. Need Recognition
- Definition: The initial stage where the consumer identifies a gap between their current state and a desired state. This is the trigger that initiates the buying process.
-
Triggers:
- Internal Stimuli: Basic needs like hunger, thirst, or fatigue.
- External Stimuli: Marketing efforts (ads, promotions), social influences, or changes in circumstances.
-
Examples:
- Running shoes wear out (problem recognition).
- Seeing a stylish new outfit online (want recognition).
- Feeling hungry (basic need recognition).
2. Information Search
- Definition: Once a need is recognized, the consumer actively searches for information about potential solutions.
-
Sources:
- Internal Sources: Past experiences, memories, and personal knowledge.
-
External Sources:
- Personal sources (friends, family, colleagues).
- Commercial sources (advertising, websites, salespeople).
- Public sources (consumer reports, reviews).
- Experiential sources (product trials, samples).
-
Examples:
- Researching different brands of running shoes online.
- Asking friends for recommendations on a new restaurant.
- Reading product reviews on a retailer's website.
3. Evaluation of Alternatives
- Definition: Consumers compare various products or brands based on their criteria and needs. They assess the pros and cons of different options.
-
Evaluation Criteria:
- Features, benefits, and quality.
- Price and value.
- Brand reputation.
- Convenience and availability.
- Personal preferences and values.
-
Examples:
- Comparing different brands of smartphones based on price, camera quality, and battery life.
- Evaluating different models of cars based on fuel efficiency, safety ratings, and features.
- Deciding between different types of coffee based on taste, origin, and price.
4. Purchase Decision
- Definition: The stage where the consumer makes a purchase choice based on their evaluation.
-
Influencing Factors:
- Availability of the product.
- Payment options and financing.
- Store atmosphere and shopping experience.
- Unexpected situations.
-
Examples:
- Choosing a specific brand of sneakers and adding them to a shopping cart.
- Deciding to go to a particular restaurant because it has available tables.
- Making a final decision to buy a car after test driving it.
5. Post-Purchase Behavior
- Definition: The consumer assesses their satisfaction and makes a judgment about their purchase after the transaction.
-
Key Aspects:
- Customer satisfaction or dissatisfaction.
- Cognitive dissonance (buyer's remorse).
- Word-of-mouth recommendations.
- Brand loyalty and future purchases.
-
Examples:
- Feeling happy with the new phone purchase and recommending it to others.
- Experiencing buyer's remorse after buying a product that does not meet expectations.
- Leaving a positive review for a product online and becoming a repeat customer.
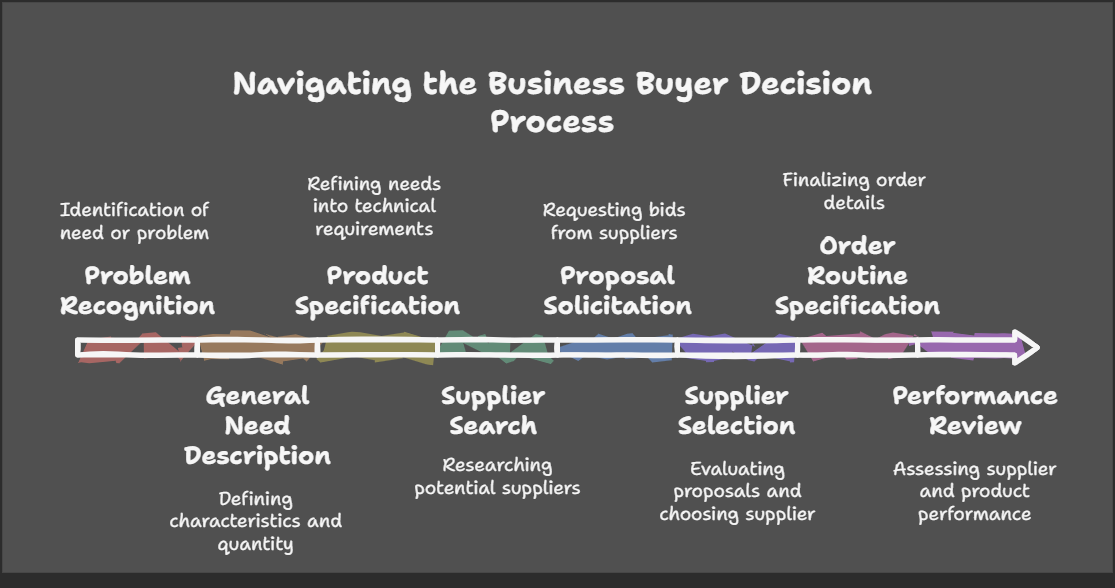
Business Buyer Decision Process - 8 Steps
This document outlines the eight-step process that businesses typically follow when making a purchasing decision.
1. Problem Recognition
-
Description: The process begins when a need or problem is identified within the organization. This can be triggered by various factors, such as:
- Shortage of existing supplies
- Dissatisfaction with current products or services
- New business opportunities requiring new resources
- Technological advancements
- Changes in regulations
- Outcome: Clear articulation of the need or problem.
2. General Need Description
- Description: Once the problem is recognized, the buyer defines the characteristics and quantity of the item(s) needed. This is a broad description and does not specify particular brands or suppliers.
- Focus: Defining general requirements, functions, and specifications.
- Example: "We need new office chairs for our employees" instead of "We need the ergonomic X brand chairs".
- Outcome: A general understanding of what is required to address the identified problem.
3. Product Specification
- Description: The buyer now refines the general need into specific technical requirements for the product or service. This includes detailed specifications, features, and performance criteria.
- Focus: Technical requirements, quality standards, and desired functionalities.
- Example: Specifying the material, adjustability, dimensions, and load capacity for the office chairs.
- Outcome: A clear and detailed set of specifications that suppliers can use to propose solutions.
4. Supplier Search
-
Description: The buyer actively researches and identifies potential suppliers capable of meeting the specified needs. This involves various methods:
- Online search
- Trade directories
- Industry contacts
- Recommendations from other businesses
- Attending trade shows
- Focus: Finding suppliers that have a track record of reliable and quality products.
- Outcome: A shortlist of potential suppliers.
5. Proposal Solicitation
- Description: The buyer formally requests proposals or bids from the shortlisted suppliers. This outlines the specific requirements and evaluation criteria.
- Focus: Gathering detailed offers, including pricing, delivery schedules, warranties, and any other pertinent information.
- Outcome: Received proposals from the selected suppliers.
6. Supplier Selection
-
Description: The buyer evaluates the received proposals based on predefined criteria, which can include:
- Price
- Quality
- Delivery time
- Supplier reputation
- After-sales service
- Financial stability
- Focus: Choosing the supplier that offers the best overall value and meets the organization's needs.
- Outcome: Selection of a chosen supplier and agreement on terms.
7. Order Routine Specification
-
Description: The buyer finalizes the order, specifying:
- Technical specifications
- Quantity
- Delivery schedule
- Payment terms
- Return policies (if any)
- Focus: Formalizing the agreement and clearly outlining expectations for both parties.
- Outcome: A formal purchase order is issued.
8. Performance Review
- Description: After receiving and using the product/service, the buyer conducts a post-purchase evaluation to assess supplier performance, product quality, and overall satisfaction.
-
Focus:
- Confirming whether the product/service meets the requirements
- Identifying areas for improvement in the future
- Assessing if they will use this supplier again for repeat purchases
- Outcome: Insights and feedback are used for future purchasing decisions and supplier relationship management.