Consumer Behavior Model (Black Box)
Definition of Consumer Behavior
Consumer behavior is the study of individuals and groups to understand the process they follow before making a purchase. It includesencompasses psychological, social, and cultural factors that influence decision-making.
According to Engel, Blackwell, and Mansard:
"Consumer behavior is the actions and decision processes of people who purchase goods and services for personal consumption."
Black Box Model of Consumer Behavior
The Black Box Model explains how external stimuli are processed in the consumer's mind (referred to as the "black box") to result in a purchase decision or response. It focuses on three main components:
-
Environment
, -
Buyer's Black Box
,and -
Buyer's
ResponseResponses.
1. Environment
The environment consists ofincludes external factors that influence a consumer’sconsumer behavior.
Marketing include:Stimuli
-
MarketingProduct:Stimuli:RefersProduct,toPrice,thePlace,features,Promotion.quality, and design of a product that make it desirable. - Price: The monetary cost of the product and how it aligns with perceived value.
- Place: The channels through which a product is distributed and its availability.
- Promotion: Advertising, discounts, or other marketing tactics used to attract consumers.
Other External Factors:
-
Political,EconomicCultural,Factors: Consumer income, inflation, and market conditions that affect buying capacity. - Technological Factors: Innovations that improve product appeal, accessibility, or functionality.
- Political Factors: Laws, government policies, and trade regulations that impact the market.
- Cultural Factors: Shared beliefs, traditions, and norms influencing what consumers prioritize.
-
Social
influences.Factors: Influence from social circles such as family, friends, and communities.
2. Buyer's Black Box
The buyer's black box refers torepresents the internal mental processes withinthat thedrive consumer’s mind, which are not directly observable.decisions. It includes two mainprimary aspects:
(a) Buyer's Characteristics
Beliefs,attitudes, values,Beliefs andmotivations.Attitudes: The ideas and feelings a consumer holds about a product or service.Knowledge,perceptions,Values andlifestyle.Motivations: The internal drivers such as aspirations, goals, or desires that shape decisions.ThesefactorsKnowledgeshapeand Perceptions: What consumers know about a product and howthetheybuyerperceiveprocessesitsinformationusefulness.-
Lifestyle: The way consumers live, their habits, and
makespreferences,decisions.which impact their choices.
(b) Buyer's Decision Process
The decision-making process includes the following steps:
-
Problem
RecognitionRecognition::
IdentifyingThis is the first step, where the consumer identifies aneedgap between their current situation and a desired state. For example, feeling hungry or needing aproblem.new phone. -
Information
SearchSearch::
GatheringThe consumer gathers information aboutsolutions.potential solutions from various sources, such as advertisements, reviews, or word-of-mouth recommendations. -
Evaluation of
AlternativesAlternatives::
ComparingThe consumer compares different products orservices.services based on factors like price, quality, and features to decide which best meets their needs. -
Purchase
DecisionDecision::
DecidingThewhatconsumertoselectsbuya product, brand, andfromretailer.where.The decision is influenced by past experiences, preferences, and any current promotions. -
Post-Purchase
EvaluationEvaluation::
ReflectingAfter the purchase, the consumer reflects onthetheirpurchasedecision.experience.Positive experiences can lead to satisfaction and loyalty, while negative ones may cause dissatisfaction or regret.
3. Buyer's Responses
The buyer's responses include:are the observable outcomes of the internal decision-making process.
Purchase Decisions
:What- Consumers decide what product to buy, which
brand,brand to choose, andfromwherewhere.to make the purchase.
Behavioral Reactions
:Loyalty,- Post-purchase
switching,behavior includes loyalty to the brand, switching to another brand, or experiencing buyer’s remorse(regretifafterthepurchase).product does not meet expectations.
brandNo Purchase
:The- Sometimes, the consumer may decide not to buy at all if the product
doesn’tfailsmeettothealignbuyer’swithexpectationstheir needs, budget, orneeds.expectations.
decisionBuyer'sResponses
Buyer'sSummary
ResponsesofEnvironment Environment Purchase Decisions Purchase Decisions Marketing Stimuli Marketing Stimuli Behavioral Reactionsthe Black Box Modelof Consumer Behavior Black Box Model of Consumer Behavior Behavioral Reactions Other External Factors Other External Factors No Purchase No Purchase Buyer's Black Box Buyer's Black Box Buyer's Characteristics Buyer's Characteristics Buyer's Decision Process Buyer's Decision Process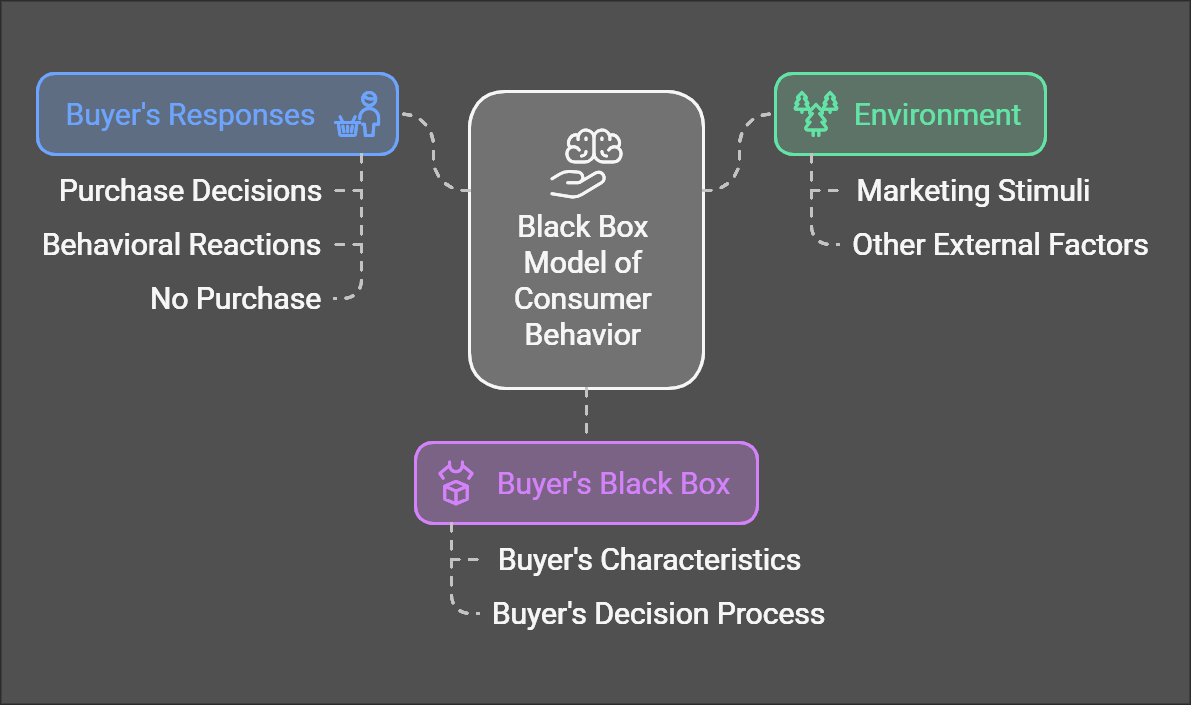
- Consumers decide what product to buy, which
The Black Box Model provides a structured way to analyze the interaction between external stimuli, internal decision-making processes, and observable buyer responses. It helps marketers understand howconsumer consumers make decisionsbehavior and tailor theircreate strategies to influence buyingpurchasing behaviordecisions effectively.
