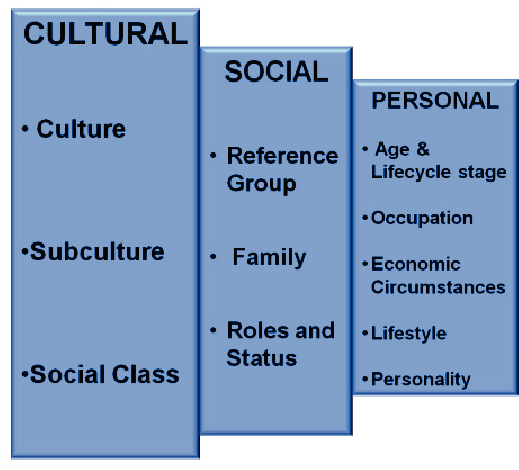
Factors Affecting Consumer Behavior
1. Cultural Factors
Cultural factors play a significant role in shaping a consumer's behavior:
-
Culture: The values, beliefs, and traditions a person grows up with influence their purchasing decisions.
- Example: In some cultures, gifting during festivals is a common practice, influencing the demand for specific products.
-
Subculture: Smaller groups within a culture, like religious, regional, or ethnic groups, can also shape buying habits.
- Example: A person belonging to a specific subculture may prefer products that align with their traditions or beliefs.
-
Social Class: A person’s social class (lower, middle, upper) affects the type of products they buy and their preferences.
- Example: Higher social classes may opt for luxury items, while middle-class consumers may focus on affordability.
2. Social Factors
-
Family: Family members play a major role in influencing buying decisions.
- Example: Parents may prioritize spending on their children’s education or toys.
-
Reference Groups: Groups like friends, coworkers, or influencers guide consumer preferences and choices.
- Example: A person might buy a product recommended by their peers or a celebrity they admire.
-
Roles and Status: A person’s position in society or within a group affects their purchases.
- Example: A manager may buy formal attire for work, while a student might focus on casual wear.
3. Personal Factors
Personal characteristics unique to an individual shape their buying behavior:
-
Age and Life Cycle: A person’s age and stage in life affect their needs and purchases.
- Example: Young adults might spend more on gadgets, while older individuals may focus on healthcare products.
-
Occupation: A person’s job influences their buying habits.
- Example: A doctor might buy medical equipment, while a construction worker may focus on tools.
-
Economic Situation: A consumer’s income and savings determine what they can afford.
- Example: Someone with a high income may buy premium products, while others may seek budget-friendly options.
-
Lifestyle: The way a person lives (activities, interests, opinions) shapes their buying patterns.
- Example: A fitness enthusiast may spend more on gym memberships and healthy foods.
-
Personality: Individual traits like confidence, dominance, or introversion can affect buying preferences.
- Example: A confident person might prefer bold, unique products.
These factors collectively influence why and how consumers make their purchasing decisions.