Anyone can be an Entrepreneur
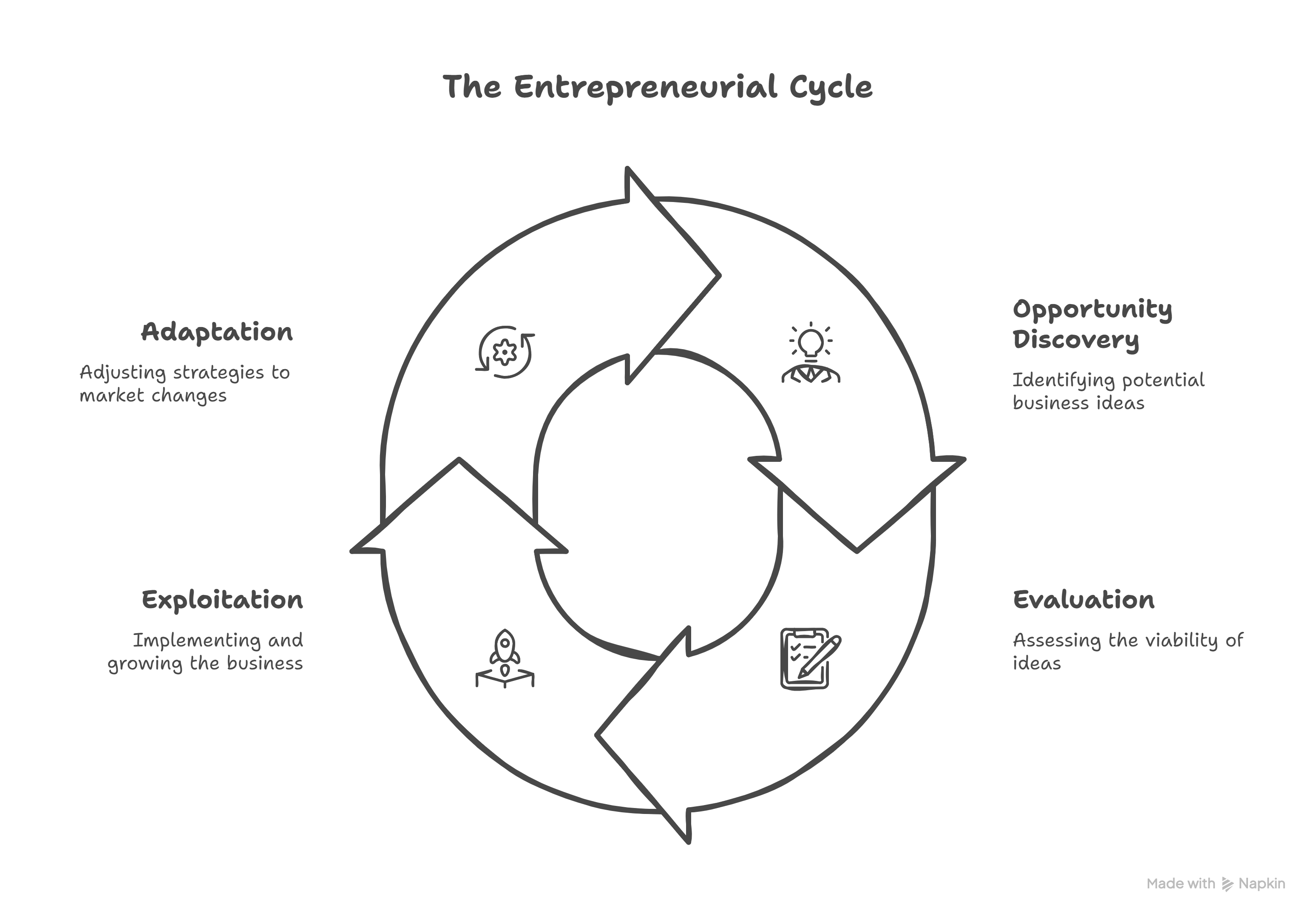
Entrepreneurship involves creating future goods/services through opportunity discovery, evaluation, and exploitation. It is not limited to a linear process or innate traits—anyone can learn and adapt to its dynamic nature.
Core Concepts
1. Entrepreneurship Defined
-- Creation of the Future
Building something entirely new (e.g., e-curtains that adapt to sunlight using embedded electronics).
Not just ideas: Requires execution—supply chains, pricing, distribution.
-- Method vs. Process
- Linear Process (e.g., college fest planning): Sequential steps with predictable outcomes.
- Entrepreneurial Method: Flexible toolkit (experimentation, iteration) to navigate uncertainty.
2. Risk vs. Uncertainty
Jar Experiment Analogy
- Jar 1 (Risk): Predictable objects (Snickers, Ferrero Rocher).
- Implication: Known probabilities (e.g., fest budgets based on past data).
- Jar 2 (Uncertainty): Unpredictable objects (lemon, ping-pong ball).
- Implication: Unknowable outcomes (e.g., launching e-curtains with no market history).
-
Key Difference:
- Risk = Predictable with data.
- Uncertainty = Requires constant learning (e.g., testing prototypes).
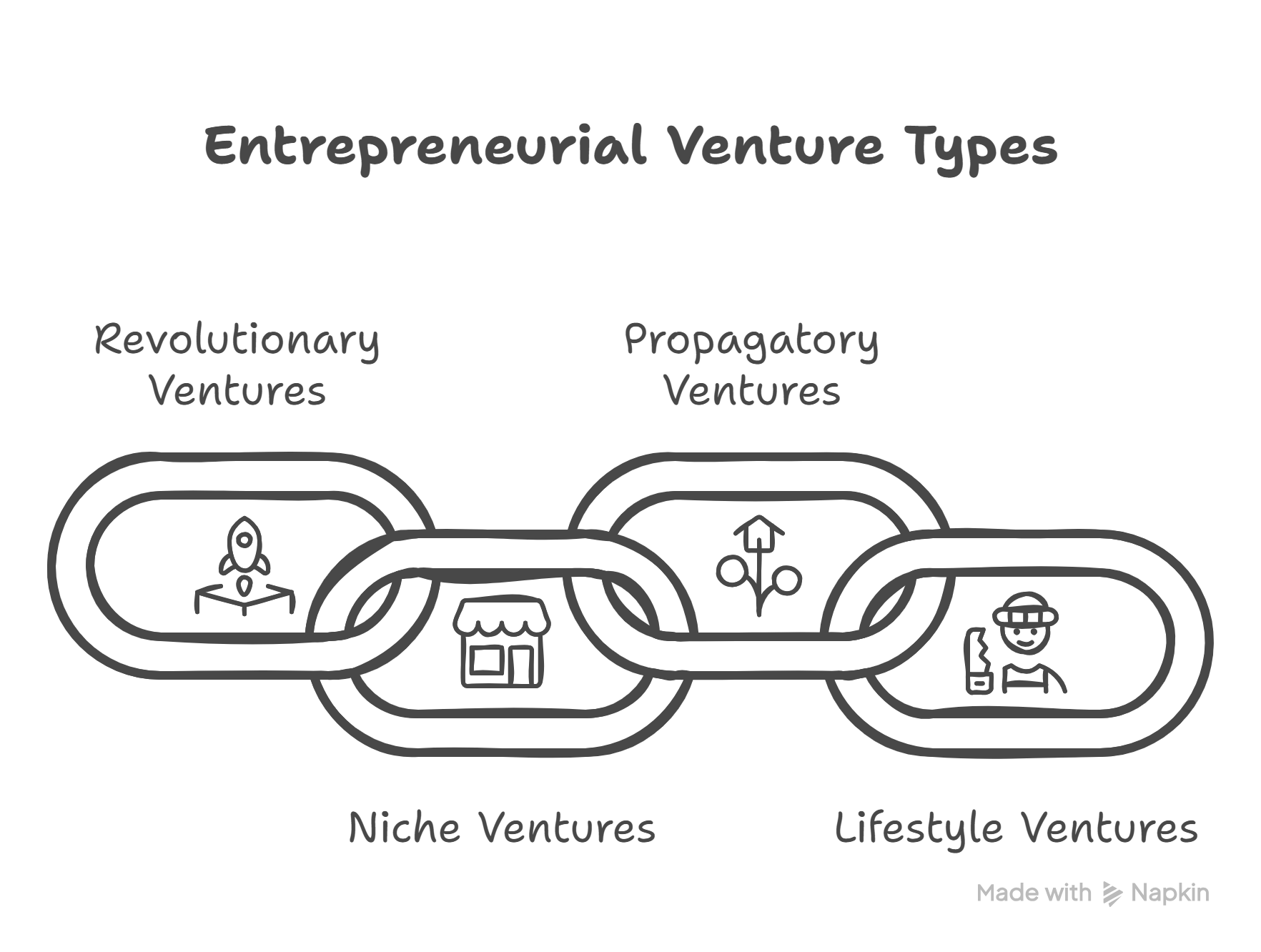
Types of Entrepreneurial Ventures
| Venture Type | Definition | Examples | Main Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revolutionary | Zero-to-One innovation | • E-curtains (electronic textiles) • SpaceX reusable rockets |
High uncertainty, resource-intensive |
| Niche | Specialized, small market | • Vegan food brands • Antiquities trading platforms |
Limited scalability |
| Propagatory | Adapt existing models to new contexts | • Flipkart’s cash-on-delivery (inspired by Amazon) • Turo (car-sharing) |
Cultural & contextual adaptation |
| Lifestyle | Built around founder’s personal skills | • Design studios • Boutique accounting firms |
Reliant on founder’s capabilities |
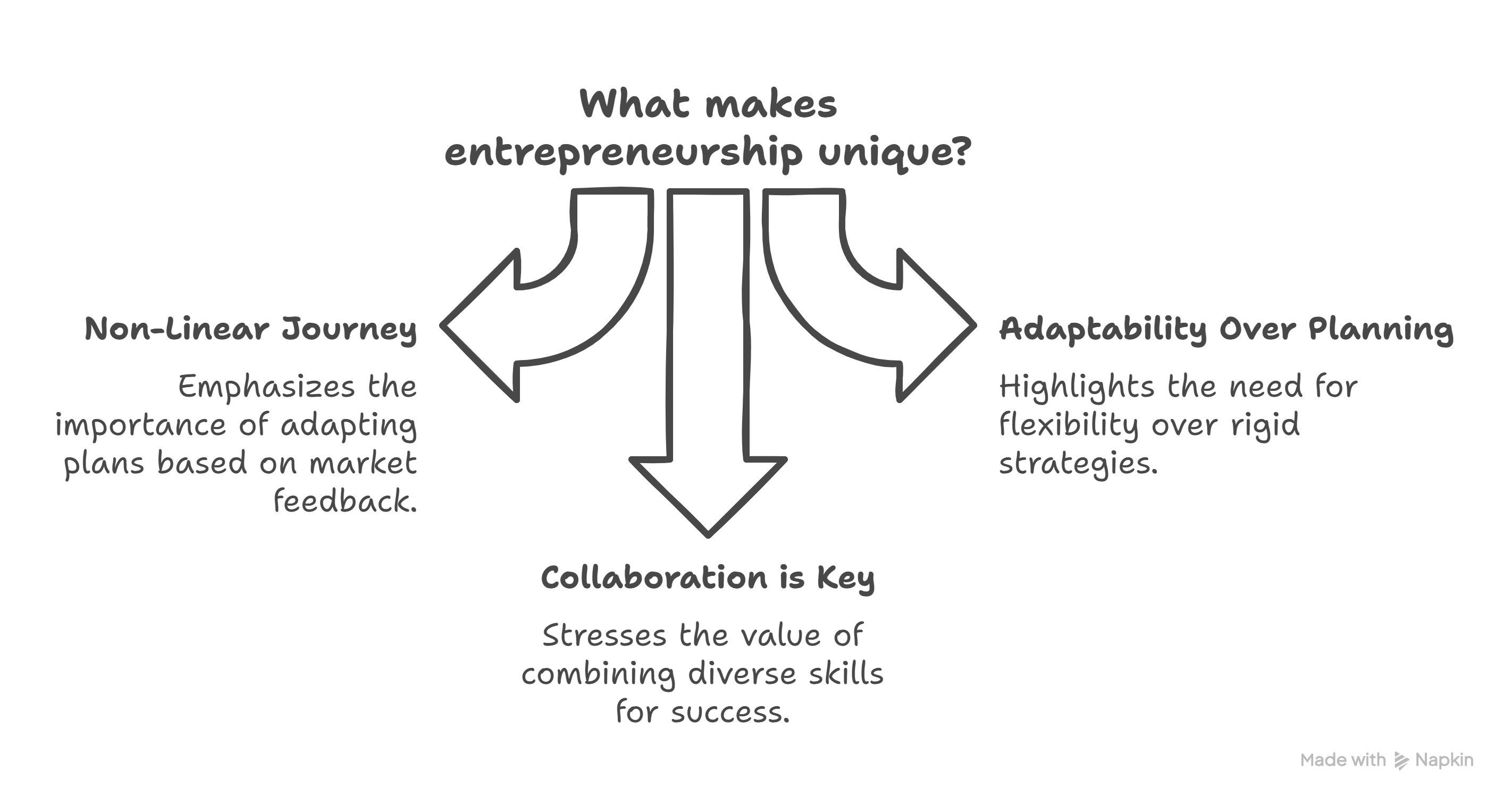
Why Entrepreneurship Is Unique
-
Non-Linear Journey
- Example: Flipkart pivoted to COD despite copying Amazon.
- Insight: Plans evolve based on real-time feedback.
-
Adaptability Over Planning
- Example: ID Fresh Foods moved from IT to perishable-food logistics via trial-and-error.
- Insight: Flexibility trumps rigid strategies.
-
Collaboration Is Key
- Example: Tricog Health combined cardiology expertise with AI partners for diagnostic tools.
- Insight: Diverse teams bridge skill gaps (tech + domain knowledge).
[ ]
]
Key Takeaways
- Method Over Process: Leverage experimentation & iteration.
- Venture Diversity: Pick your type (revolutionary, niche, propagatory, lifestyle) to match goals.
-
Uncertainty ≠ Risk:
- Uncertainty demands adaptability.
- Risk uses historical data for planning.
- Learnable Skill: No “born entrepreneur”—skills develop through practice.
Examples Recap
- E-curtains: Revolutionary venture (high uncertainty).
- Flipkart: Propagatory venture (local adaptation).
- Lifestyle Studios: Founder-driven, low resource needs.

No Comments