Internationalization of Business and Finance
Internationalization of Business and Finance
This section focuses on the broader trends of internationalization in business and finance.
Defining Internationalization
- Internationalization of Business: The process of expanding business activities across national borders. Includes exporting, FDI, strategic alliances, and other forms of cross-border activity.
- Internationalization of Finance: The increasing integration of financial markets globally. Characterized by cross-border capital flows, global financial instruments, and interaction of international financial institutions.
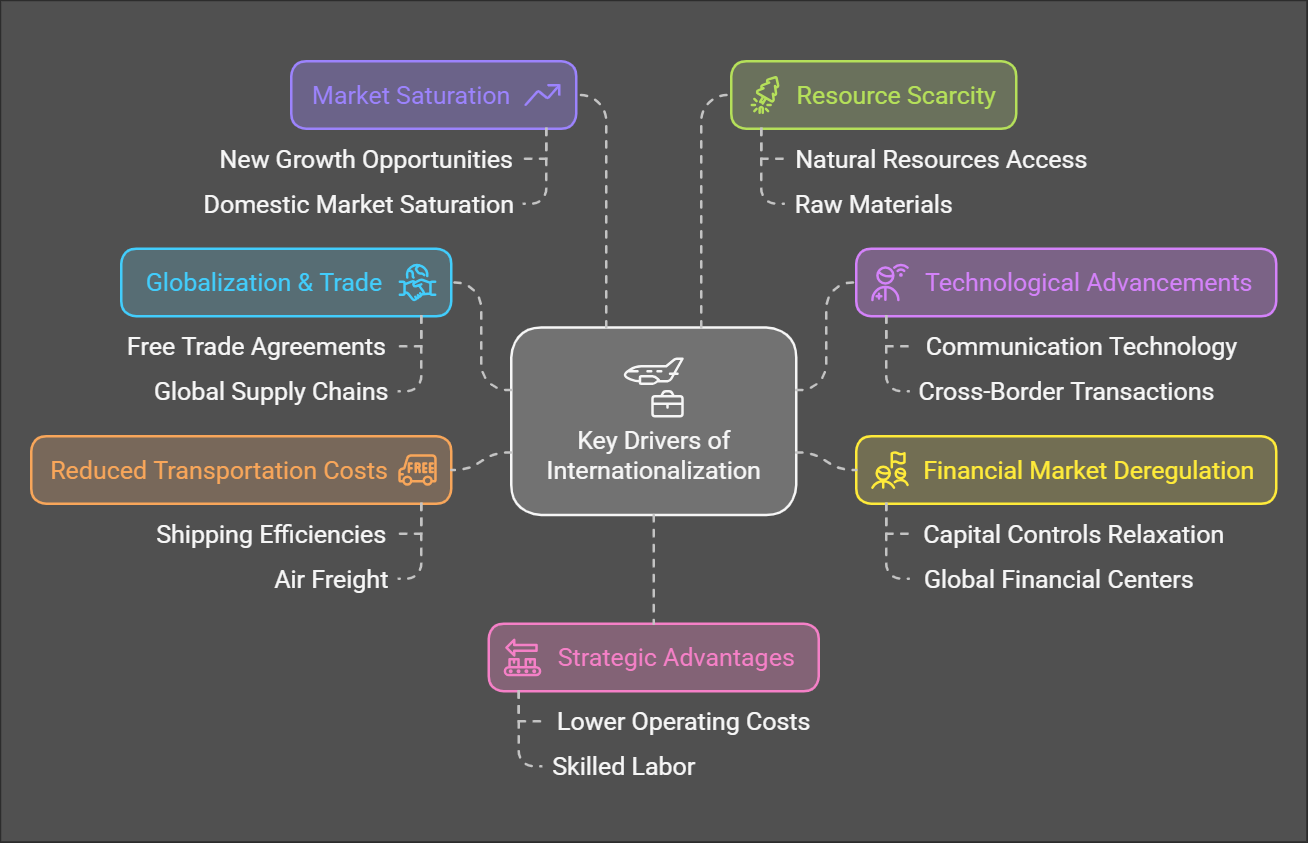
Key Drivers of Internationalization
-
Globalization & Trade:
- Reduced trade barriers and increased free trade agreements.
- Integration of national economies through global supply chains.
-
Technological Advancements:
- Improvements in communication and information technology.
- Faster and more efficient cross-border transactions.
-
Financial Market Deregulation:
- Relaxation of capital controls and free movement of funds.
- Growth of global financial centers and instruments.
-
Reduced Transportation Costs:
- Efficiencies in shipping, air freight, and logistics.
- Lower cost of transporting goods across borders.
-
Market Saturation:
- Seeking new growth opportunities outside of saturated domestic markets.
-
Resource Scarcity:
- Accessing natural resources and raw materials not available domestically.
- Strategic Advantages:
Forms of Internationalization
- Exporting: Selling goods and services to foreign markets.
- Importing: Sourcing goods and services from foreign markets.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Investing directly in foreign operations and assets.
- Strategic Alliances and Joint Ventures: Partnering with foreign companies for specific projects.
- Licensing and Franchising: Granting foreign companies the right to use intellectual property or business models.
- Portfolio Investment: Investing in foreign stocks, bonds, and other financial assets.
- International Banking: Providing financial services across national borders.
Impact of Internationalization
- Increased Trade: Growth in global trade volumes and trade flows.
- Capital Flows: Movement of capital across national borders.
- Global Supply Chains: Complex interconnected production networks.
- Financial Integration: Greater interaction between financial institutions and markets.
- Economic Interdependence: Increased reliance of economies on one another.
- Technological Diffusion: Spreading technology and innovation across countries.
- Cultural Exchange: Increased interaction and exchange of ideas across different cultures.
Challenges and Risks
- Economic Volatility: Increased exposure to global economic shocks.
- Financial Crises: Potential for systemic risks and contagion effects.
- Political Instability: Geopolitical conflicts and protectionist policies.
- Cultural Misunderstandings: Issues related to cultural differences.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating diverse legal and regulatory systems.

No Comments