The Economic Cycle and Economic Policy
The Economic Cycle and Economic Policy
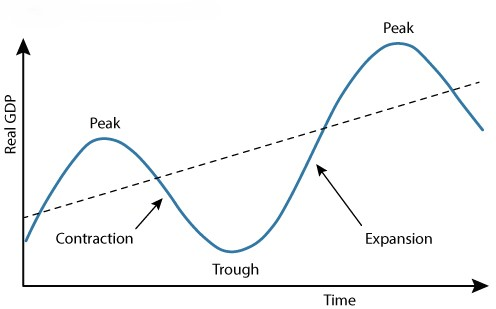
The Economic Cycle (or Business Cycle)
The economic cycle refers to the fluctuations in economic activity that an economy experiences over time. It's a recurring pattern of expansion and contraction. Think of it like a rollercoaster ride for the economy.
Stages of the Economic Cycle:
-
Expansion (or Boom):
- What's happening? The economy is growing.
-
Characteristics:
- Rising employment and falling unemployment.
- Increased production of goods and services.
- Higher consumer spending and business investment.
- Rising prices (inflation might start to appear).
- General optimism and confidence in the economy.
- Think of it as: The upward climb of the rollercoaster.
-
Peak:
- What's happening? The highest point of economic activity in the current cycle.
-
Characteristics:
- Economy is operating at full or near full capacity.
- Inflation may be high.
- Possible over-investment and speculative behavior.
- Economy is vulnerable to a downturn.
- Think of it as: Reaching the top of the rollercoaster before going down.
-
Contraction (or Recession/Downturn):
- What's happening? The economy is slowing down.
-
Characteristics:
- Falling employment and rising unemployment.
- Decreased production of goods and services.
- Reduced consumer spending and business investment.
- Falling prices (or lower inflation).
- Pessimism and uncertainty in the economy.
- Think of it as: The downward drop of the rollercoaster.
-
Trough:
- What's happening? The lowest point of economic activity in the current cycle.
-
Characteristics:
- High unemployment and low economic activity.
- Economy is at its weakest point, before a recovery.
- Think of it as: Reaching the bottom of the rollercoaster.
- Recovery:
Why does the Cycle Happen?
- Changes in Demand: Shifts in consumer spending, business investment, and government expenditure.
- Changes in Supply: Disruptions to production (e.g., natural disasters, resource shortages).
- Market Sentiment: Optimism and pessimism can drive booms and busts.
- Government Policies: Fiscal and monetary policies can influence the cycle.
Economic Policy
Economic policy refers to actions taken by governments to influence the economy. The main goals are to:
- Promote sustainable economic growth.
- Maintain price stability (control inflation).
- Achieve full employment (reduce unemployment).
- Reduce inequality.
Types of Economic Policy:
-
Fiscal Policy:
- What is it? Government actions related to spending and taxation.
-
Tools:
- Government Spending: Increases or decreases in spending on infrastructure, social programs, etc.
- Taxation: Changes in tax rates to influence income, investment, and consumption.
- Examples: Increasing government spending during a recession or cutting taxes to stimulate the economy.
-
Monetary Policy:
- What is it? Central bank actions to control the money supply and interest rates.
-
Tools:
- Interest Rates: Raising or lowering interest rates to affect borrowing costs.
- Money Supply: Controlling the amount of money in circulation.
- Examples: Reducing interest rates during a recession to encourage borrowing and investment.
-
Supply-Side Policies:
- What is it? Government actions aimed at increasing the productive capacity of the economy.
-
Tools:
- Deregulation: Reducing bureaucracy to make it easier to start a business
- Education & Training: Programs to improve workforce skills.
- Tax Cuts: Reducing corporation taxes to incentivise investment and job creation
- Examples: Providing tax incentives for businesses to invest in research and development, or training programs to increase skills
-
Trade Policies:
- What is it? Government actions that impact international trade, and how an economy integrates with the rest of the world
-
Tools:
- Tariffs : Taxes on imported goods, can protect some domestic industries.
- Quotas: Placing limits on imported goods, also used to protect domestic industries.
- Trade agreements : Agreements with other nations on reduced trade restrictions, promotes increased trade.
- Examples Implementing tariffs on imported goods to protect the domestic industry.
How Policies Interact with the Cycle:
- During Recessions: Governments might use expansionary fiscal policy (increased spending, tax cuts) and expansionary monetary policy (lower interest rates) to stimulate the economy and promote recovery.
- During Booms: Governments might use contractionary fiscal policy (reduced spending, higher taxes) and contractionary monetary policy (higher interest rates) to cool down the economy and prevent overheating (high inflation).
In Summary
Understanding the economic cycle helps us see how economies fluctuate. Economic policies are the tools governments use to try and smooth out these fluctuations and achieve desired economic outcomes. It's important to know that policies are not always perfect, and they can have unintended consequences.

No Comments