Classification of Production System
Classification of Production
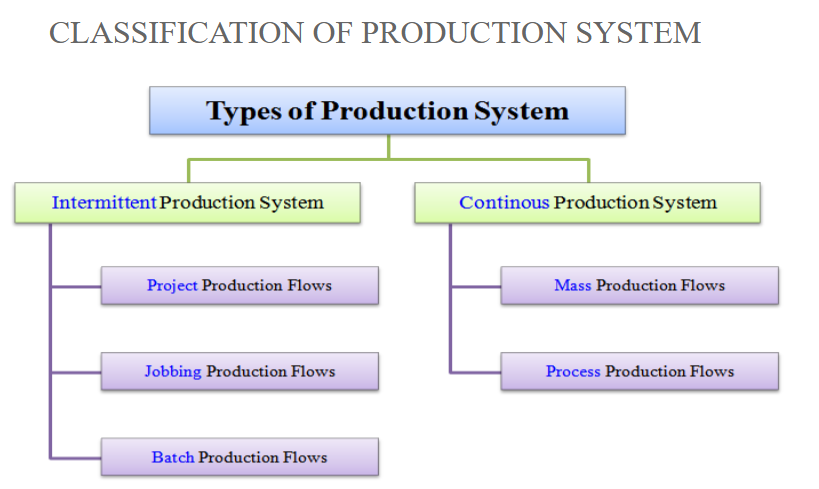
1. Intermittent Production Systems
-
Characteristics:
- Produce goods in batches or runs, with periods of production followed by periods of no production.
- Low to medium production volume.
- High product variety.
- Flexible to accommodate changes in customer demand.
- Longer lead times due to batch processing and setup times.
- Requires more inventory management to handle fluctuations in production and demand.
-
Examples:
- Custom furniture manufacturing
- Job shops producing specialized products
- Printing and publishing
2. Continuous Production Systems
-
Characteristics:
- Produce goods in a continuous flow, without interruptions.
- High production volume.
- Standardized products with limited variety.
- Shorter lead times due to continuous flow.
- Efficient and cost-effective for large-scale production.
- Requires a stable supply chain to ensure uninterrupted production.
-
Examples:
- Steel mills
- Chemical plants
- Oil refineries
Within Intermittent Production Systems:
-
Project Production Flows:
- Involve producing a single, large-scale project with a defined scope and timeline.
- Examples: Construction of bridges, ships, aircraft.
-
Jobbing Production Flows:
- Produce small quantities of customized products based on specific customer orders.
- Examples: Tailoring, repair services, custom jewelry.
-
Batch Production Flows:
- Produce goods in batches or lots, with each batch having a similar configuration.
- Examples: Pharmaceuticals, food processing, furniture manufacturing.
Within Continuous Production Systems:
-
Mass Production Flows:
- Produce large quantities of standardized products using highly automated processes.
- Examples: Automobiles, consumer electronics, beverages.
-
Process Production Flows:
- Used for industries with continuous processes, such as chemicals, oil, and gas.
Key Considerations for Choosing a Production System:
- Product characteristics: Volume, variety, customization requirements.
- Demand patterns: Predictability and stability of demand.
- Cost: Production costs, inventory costs, setup costs.
- Lead time: Time required to produce and deliver products.
- Flexibility: Ability to adapt to changes in demand or product specifications.
- Quality: Need for high-quality standards.
- Resource availability: Availability of skilled labor, capital, and equipment.

No Comments