Dividend policy decisions - meaning and significance , kinds of dividends, bonus shares.
Dividend Policy Notes
I. Dividend Policy Decisions: Meaning and Significance
Definition: Decisions by a company's board on the amount, form, and timing of cash distributions to shareholders from profits. Determines how much of earnings is paid out versus retained for reinvestment.
Significance:
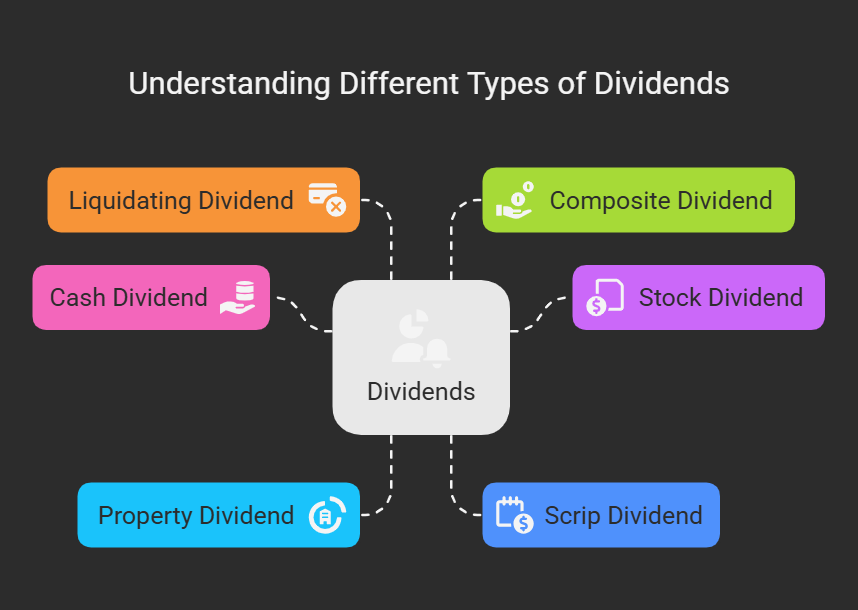
II. Kinds of Dividends
- Cash Dividend: Most common, paid in cash. Requires sufficient cash.
- Stock Dividend (Bonus Shares): Paid in additional shares. No cash outflow. Increases outstanding shares, reduces per-share price.
- Property Dividend: Paid in assets other than cash. Rare due to valuation/tax complications.
- Scrip Dividend (Deferred Dividend): Promissory note to pay dividend later. Used when cash is currently lacking but expected in the future.
- Liquidating Dividend: Return of capital to shareholders during liquidation. Distribution of assets, not earnings.
- Composite Dividend: Partly cash and partly in kind.
III. Bonus Shares (Stock Dividends)
Meaning: Distribution of accumulated profits as free additional shares to existing shareholders, proportionally to their holdings.
Merits:
- Preserves Cash: Conserves cash for reinvestment.
- Signaling Effect: Signals confidence in long-term prospects.
- Increased Marketability: Reduces per-share price, making stock affordable, potentially increasing trading volume.
- Enhanced Investor Confidence: Shareholders can profit from price rise after announcement.
- May Prevent Hostile Takeovers: Expands ownership base.
Demerits:
- Dilution of Earnings per Share (EPS): Increases shares outstanding, potentially reducing EPS.
- Psychological Impact: Negative if underlying performance is not strong.
- Tax Implications: Sale of bonus shares subject to capital gains tax.
- No Real Value Creation: Divides existing equity among more shares. Market price should adjust.
Accounting Treatment: Issued by capitalizing reserves (retained earnings, general reserve, security premium).
Legal Requirements (India):

No Comments