What is Services Marketing
Services Marketing
Services and Unique Characteristics of Services
What Are Services?
- Definition: A service is an intangible activity or benefit that a business offers to fulfill the needs or wants of customers. Unlike physical products, services cannot be stored or owned.
-
Key Features:
- Services involve performance or experience.
- They are typically consumed at the point of delivery.
Examples of Services:
- Healthcare (e.g., doctor consultations).
- Education (e.g., online courses).
- Hospitality (e.g., hotel stays).
- Financial services (e.g., banking or insurance).
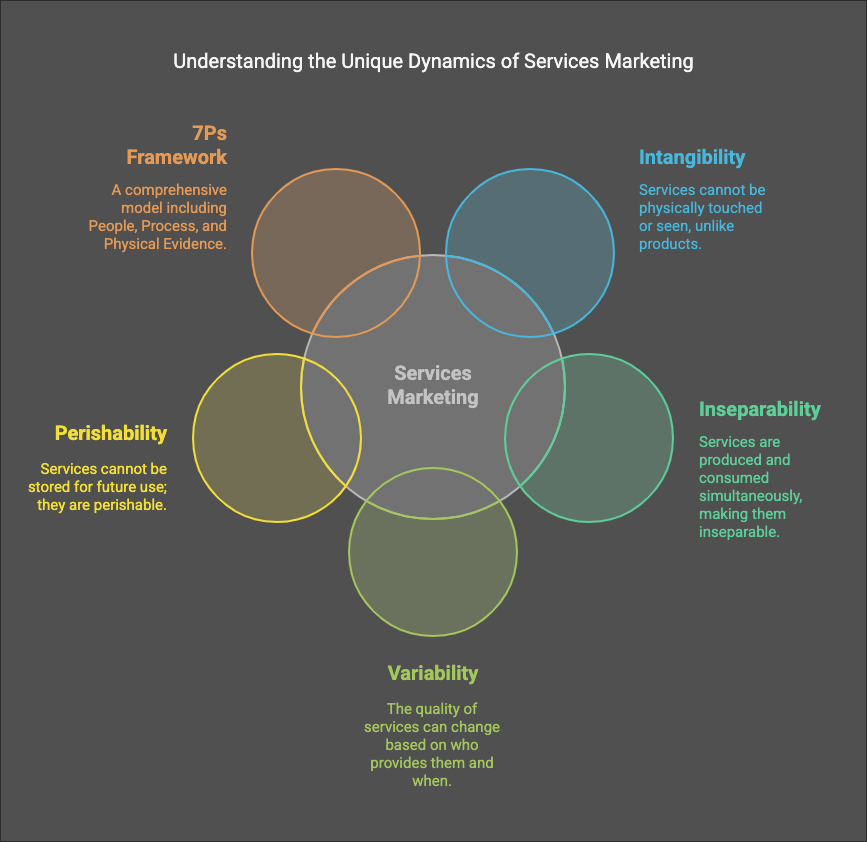
Unique Characteristics of Services
Services have six key characteristics that differentiate them from physical products:
1. Intangibility
- Definition: Services cannot be touched, seen, or physically possessed like a product.
- Implication: Customers rely on trust, brand reputation, and service quality before purchase.
- Example: A customer buying insurance does not receive a physical product but peace of mind.
2. Inseparability
- Definition: Services are produced and consumed simultaneously and cannot be separated from the provider.
-
Implication:
- The presence of the service provider is essential.
- The quality of the service depends on the interaction between the provider and the customer.
- Example: A haircut cannot be separated from the hairdresser providing it.
3. Variability (Heterogeneity)
- Definition: The quality of a service can vary depending on who provides it, when, where, and how.
- Implication: Maintaining consistent service quality is challenging.
- Example: The experience at a restaurant may differ depending on the chef, the server, or the time of day.
4. Perishability
- Definition: Services cannot be stored, saved, or inventoried for later use.
- Implication: Any unused service capacity (e.g., an empty hotel room or missed airline seat) results in lost revenue.
- Example: A vacant seat on a flight cannot be sold after the plane departs.
5. Lack of Ownership
- Definition: Services do not result in ownership of a tangible item; instead, customers receive a benefit or experience.
- Implication: Customers pay for access to or use of the service, not for possession.
- Example: Renting a car or subscribing to streaming services like Netflix.
6. Customer Participation
- Definition: Customers play an active role in the delivery of services, making them co-creators of the service experience.
- Implication: The quality and outcome of the service can depend on customer interaction.
- Example: A fitness trainer's effectiveness depends on the client's willingness to follow their workout routine.
Summary Table of Unique Characteristics of Services
| Characteristic | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Intangibility | Cannot be touched or physically owned. | Insurance policies, legal consultations. |
| Inseparability | Produced and consumed at the same time. | Haircuts, dental treatments. |
| Variability | Quality varies depending on provider and situation. | Restaurant service, hotel experiences. |
| Perishability | Cannot be stored or inventoried for later use. | Unsold flight seats, empty hotel rooms. |
| Lack of Ownership | Customers do not own the service, only experience the benefit. | Renting a car, using a gym membership. |
| Customer Participation | Customers actively contribute to the service experience. | Personal training sessions, education. |
Why Understanding These Characteristics Matters
- Marketing Strategies: Helps tailor promotions and customer communication.
- Customer Experience: Improves service delivery by addressing variability and inseparability.
- Resource Management: Minimizes losses caused by perishability.
- Trust-Building: Compensates for intangibility by focusing on reputation and customer reviews.
Understanding these characteristics is essential for businesses offering services to design effective marketing, pricing, and operational strategies.
Service Delivery Process and Competitive Strategies
What Is the Service Delivery Process?
The service delivery process refers to the sequence of activities through which a service is provided to customers. It encompasses all interactions, touchpoints, and operational steps required to ensure the delivery of a quality service.
Key Elements of the Service Delivery Process:
- Customer Interaction: Direct engagement between customers and service providers (e.g., consultations, online interactions).
- Operational Efficiency: Internal processes that ensure timely and accurate delivery of services.
- Consistency and Quality: Ensuring the service meets customer expectations every time.
- Customer Feedback: Continuous improvement through feedback collection and analysis.
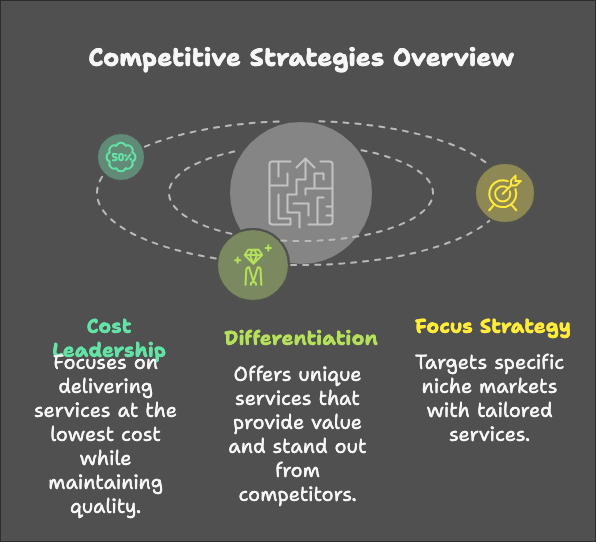
Types of Competitive Strategies (Michael Porter)
Michael Porter identified three generic competitive strategies that businesses can adopt to gain a competitive advantage in the market. These strategies apply to both products and services and are critical in shaping the service delivery process.
1. Cost Leadership
- Definition: Aiming to deliver services at the lowest cost while maintaining acceptable quality.
-
Focus:
- Reducing operational costs.
- Standardizing service delivery to minimize variability.
- Serving a large customer base at competitive prices.
-
How It Shapes Service Delivery:
- Streamlined processes to reduce delivery time and expenses.
- Use of technology (e.g., automation) to minimize labor costs.
- Efficient use of resources, such as outsourcing non-core activities.
- Example: Ryanair and Walmart focus on providing affordable travel and retail services by maintaining strict cost control measures.
2. Differentiation
- Definition: Offering unique services that provide value to customers and stand out from competitors.
-
Focus:
- Innovation and quality.
- Enhancing the customer experience.
- Building a strong brand reputation.
-
How It Shapes Service Delivery:
- Personalization of services to meet individual customer needs.
- Emphasis on superior customer service and unique features.
- Continuous improvement and investment in innovation.
- Example: Apple focuses on a premium customer experience through sleek store designs and superior technical support (e.g., Genius Bar).
3. Focus Strategy
- Definition: Targeting a specific niche market by tailoring services to meet the needs of that segment.
-
Sub-Types:
- Cost Focus: Competing on price within a niche market.
- Differentiation Focus: Offering unique services for a specific market segment.
-
How It Shapes Service Delivery:
- Specialized processes and expertise tailored to a particular audience.
- High customization to meet niche market needs.
- Focus on delivering exceptional value to a small group of customers.
- Example: Rolex targets a niche market by delivering luxury watches with exceptional craftsmanship.
Relationship Between Service Delivery Process and Competitive Strategy
The chosen competitive strategy influences how services are delivered:
-
Cost Leadership and Service Delivery:
- Processes focus on efficiency and cost reduction.
- Examples:
- Fast food chains like McDonald's rely on standardized processes.
- Airlines like Ryanair use unbundled pricing to lower costs.
-
Differentiation and Service Delivery:
- Processes emphasize uniqueness, quality, and innovation.
- Examples:
- Luxury hotels like Ritz-Carlton provide highly personalized services.
- Tech companies like Apple focus on seamless customer support.
-
Focus Strategy and Service Delivery:
- Processes are customized for a specific niche or demographic.
- Examples:
- Boutique consulting firms tailor their services to small businesses.
- Vegan restaurants focus on creating specialized plant-based menus.
Importance of Aligning Service Delivery with Competitive Strategy
-
Customer Satisfaction:
- Ensures that services meet customer expectations based on the competitive promise.
- Example: Customers expect affordability in cost leadership strategies and premium experiences in differentiation strategies.
-
Operational Efficiency:
- Aligning processes with strategy helps allocate resources effectively.
- Example: Automating routine tasks for cost leadership.
-
Sustainable Competitive Advantage:
- A clear, strategy-driven service delivery process strengthens market position.
- Example: A company with a strong differentiation focus builds customer loyalty.
Summary Table: Competitive Strategies and Service Delivery
| Competitive Strategy | Focus | Impact on Service Delivery Process | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost Leadership | Lowest cost and efficiency. | Streamlined processes, standardization, and automation. | Ryanair, Walmart. |
| Differentiation | Unique value and experience. | Personalized services, superior quality, and innovation. | Ritz-Carlton, Apple. |
| Focus Strategy | Niche market specialization. | Customized processes for niche needs. | Rolex, boutique consultants. |
By aligning the service delivery process with one of Porter’s competitive strategies, businesses can effectively serve their target audience, maintain operational efficiency, and achieve long-term success.

No Comments