Types of Buying Decision Behavior
Consumers make different types of buying decisions based on how important the purchase is to them and how much they think brands differ. Below are the four main types of buying decision behaviors explained in simple terms.
1. Complex Buying Behavior
Definition:
This happens when people are very involved in buying a product, usually because it is expensive or unfamiliar.
Characteristics:
- The decision feels risky because it costs a lot or has a big personal impact.
- Consumers spend a lot of time researching and gathering information.
- They seek advice from friends, family, or experts to make the right choice.
Example:
Buying a car for the first time is a big decision. People look at reviews, compare models, check safety features, and ask for opinions before deciding.
Marketing Implication:
Marketers need to provide detailed information about the product, highlight its benefits, and address any doubts or concerns to help the buyer feel confident in their decision.
2. Dissonance-Reducing Buying Behavior
Definition:
This happens when people care a lot about their purchase but don’t see much difference between the available brands.
Characteristics:
- The product is usually expensive or bought infrequently.
- Since the brands are very similar, people might feel unsure or worried after buying.
Example:
Choosing a folding table may involve comparing a few brands with similar designs and prices, but the decision still feels important because of the cost.
Marketing Implication:
Marketers should focus on providing good after-sale service, customer support, and warranties. This reassures buyers and makes them feel they made the right choice.
3. Habitual Buying Behavior
Definition:
This happens when people make a purchase out of habit, with little thought or effort, because they are not very involved in the decision.
Characteristics:
- People buy the same product repeatedly without comparing brands.
- Decisions are made automatically, often based on familiarity.
Example:
Buying items like toothpaste, snacks, or juice is usually a habit. People stick to the brand they’ve been using unless there’s a strong reason to switch.
Marketing Implication:
Marketers should use repetitive advertisements, discounts, and promotions to keep the brand at the top of the consumer's mind and encourage repeat purchases.
4. Variety-Seeking Buying Behavior
Definition:
This happens when people are not very involved in the purchase but notice big differences between brands, leading them to try new options for fun or variety.
Characteristics:
- Consumers switch brands often, not because they are unhappy, but because they want to try something new.
- This type of behavior is common with low-cost items.
Example:
A person might buy a different brand of cookies each time they shop just to try different flavors or textures.
Marketing Implication:
Brands should offer different options, such as trial packs or new flavors, to attract curious customers. Promotions and special offers can also encourage brand switching.
Summary
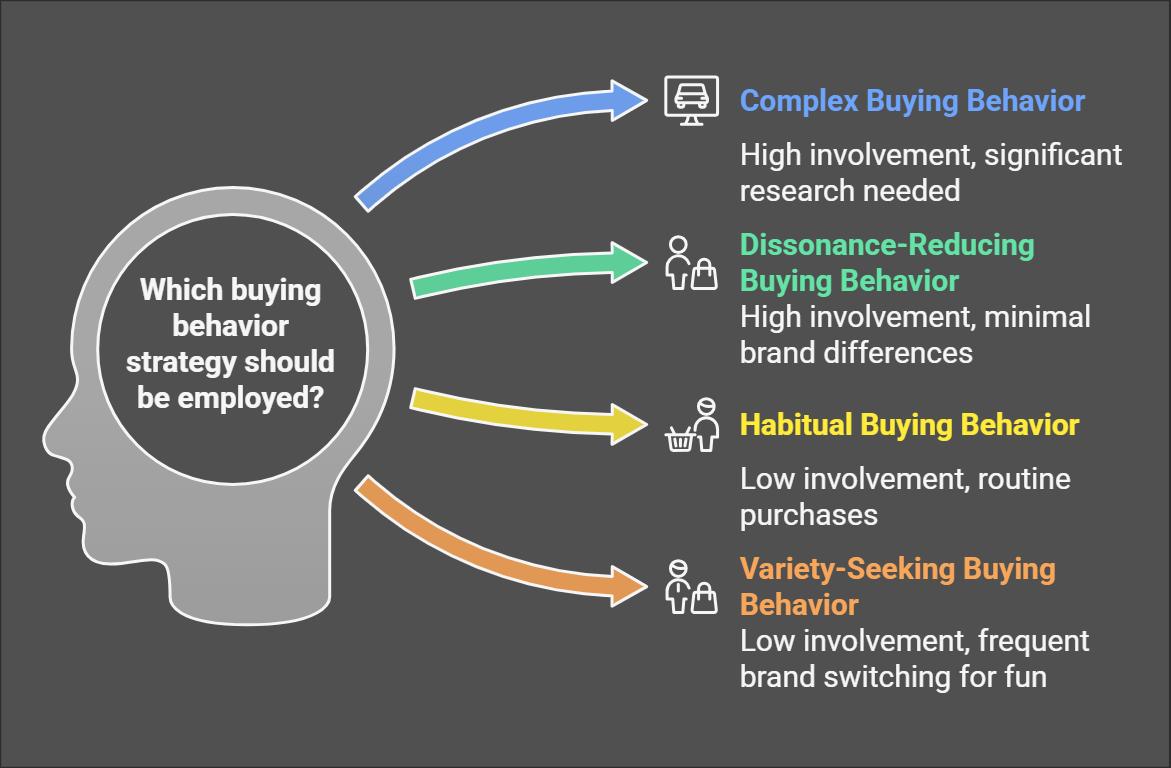
The four types of buying behaviors reflect how people think and feel when making purchases:
- Complex Buying Behavior: High involvement, significant research.
- Dissonance-Reducing Buying Behavior: High involvement, minimal brand differences.
- Habitual Buying Behavior: Low involvement, routine purchases.
- Variety-Seeking Buying Behavior: Low involvement, frequent brand switching for fun.
 Marketers can use these insights to create strategies that meet consumer needs and influence their choices effectively.
Marketers can use these insights to create strategies that meet consumer needs and influence their choices effectively.

No Comments