Introduction to Social Media Marketing (SMM)
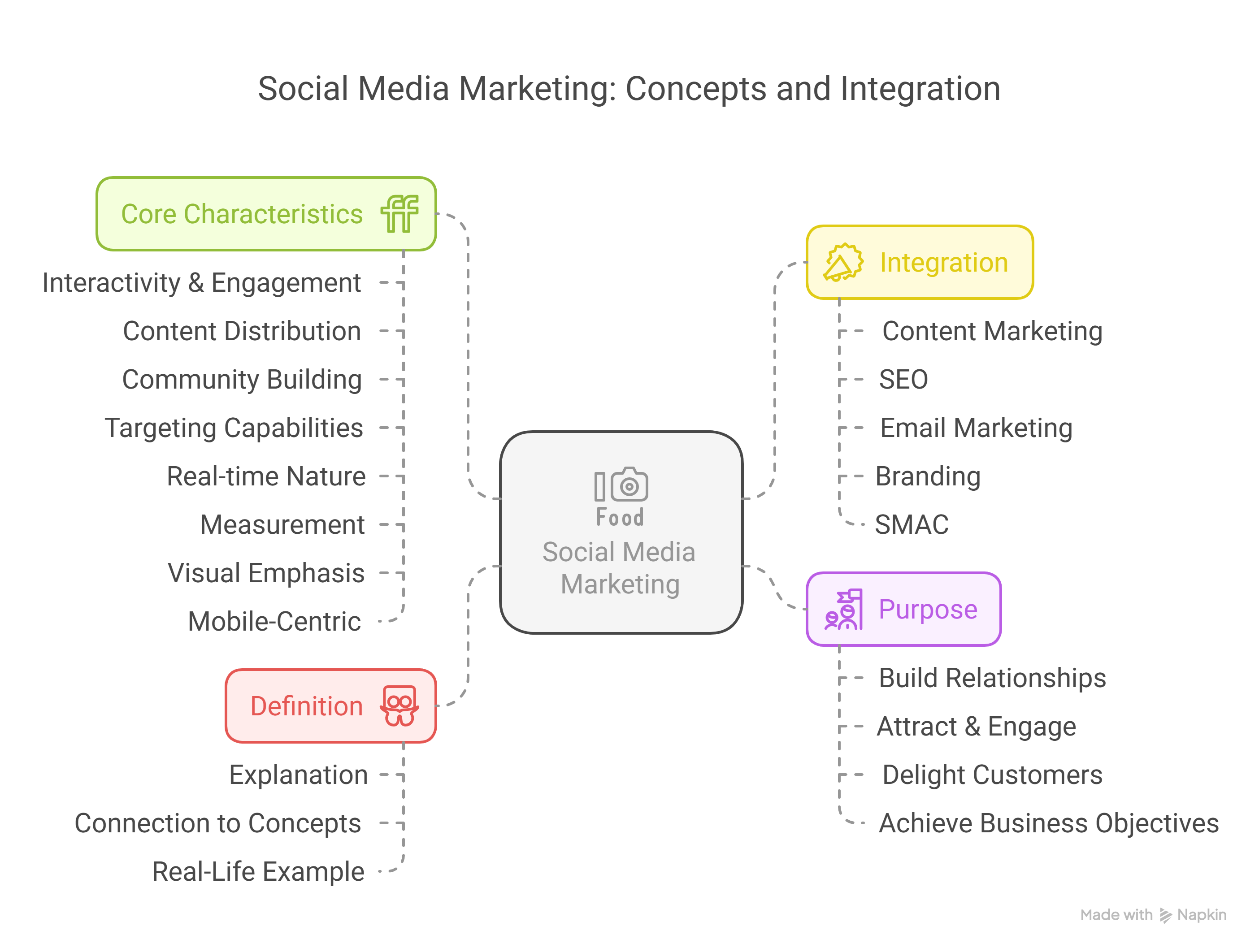
1. Definition: Social Media Marketing (SMM)
2. Purpose of SMM
-
Explanation: SMM serves several vital functions:
- Build Relationships: Foster loyalty and trust through direct interaction, responding to comments/messages, and showing brand personality.
- Attract & Engage: Use compelling content (informative, entertaining, visual) to draw in potential customers ('Attract') and keep them interested through interaction ('Engage').
- Delight Customers: Support existing customers ('Delight') through responsive service, exclusive content, or celebrating their engagement, turning them into promoters.
- Achieve Business Objectives: Drive specific goals like increasing brand awareness, generating website traffic or leads, boosting sales, and gathering customer feedback.
- Real-Life Example (Bakery): Responding to a comment asking about nut allergies builds trust (Relationships). Posting a video of frosting techniques attracts viewers (Attract/Engage). Offering an Instagram-only flash sale delights followers (Delight). Running ads for holiday pre-orders aims to boost sales (Objectives).
3. Integration of SMM
-
Explanation: SMM works best when connected with other marketing efforts:
- Content Marketing: Social media is a key distribution channel for blogs, videos, infographics, etc.
- SEO: While indirect, SMM drives traffic to optimized websites, increases brand visibility (more branded searches), and can help content earn backlinks ('Social Signals').
- Email Marketing: Use social media to grow email lists and vice-versa.
- Branding: Reinforce brand identity through consistent voice, visuals, and messaging.
- SMAC (Social, Mobile, Analytics, Cloud): SMM is the 'Social' part, working with Mobile access, performance Analytics, and Cloud infrastructure.
- Real-Life Example (Bakery): They write a blog post on "Choosing the Perfect Wedding Cake" (Content). They share it on Facebook/Pinterest (SMM) with beautiful cake photos (Branding), driving traffic to their website (helps SEO). The post includes a call-to-action to sign up for their newsletter (Email). They track clicks from social media (Analytics).
4. Core Characteristics of Social Media Platforms
-
Interactivity & Engagement:
- Explanation: Platforms are built for two-way communication (comments, shares, DMs). Brands must actively participate, respond, and foster conversation.
- Example: Bakery asks, "What new cookie flavor should we try next?" and replies to suggestions.
-
Content Distribution:
- Explanation: Act as channels to deliver diverse content formats (text, image, video, audio, links), with platforms often favoring specific types.
- Example: Bakery uses Instagram for stunning cake photos, TikTok for short decorating videos, and Facebook for event details.
-
Community Building:
- Explanation: Allow brands to gather people with shared interests, creating a loyal following connected to the brand and each other.
- Example: Bakery creates a Facebook group for local home bakers to share tips and recipes, moderated by the bakery staff.
-
Targeting Capabilities:
- Explanation: Offer sophisticated advertising options to reach specific audience segments based on demographics, interests, and behavior, increasing ad relevance and efficiency (relates to segmentation).
- Example: Bakery targets ads for kids' birthday cakes to local parents with upcoming birthdays.
-
Real-time Nature:
- Explanation: Information flows instantly, enabling timely updates, quick customer service, and participation in current conversations.
- Example: Bakery posts "Sold out of croissants for today!" to manage expectations or announces a flash sale on day-old bread.
-
Measurement (Analytics):
- Explanation: Provide built-in tools to track performance (reach, engagement, clicks, etc.), allowing data-driven optimization of strategies (the 'Analytics' in SMAC).
- Example: Bakery notices posts featuring staff get high engagement, so they plan more "Meet the Baker" content.
-
Visual Emphasis:
- Explanation: Many platforms (Instagram, Pinterest, TikTok) are highly visual. Compelling images and videos are crucial for capturing attention.
- Example: A high-quality photo of a perfectly decorated cupcake is more effective for the bakery than a text-only post.
-
Mobile-Centric:
- Explanation: Most users access social media via smartphones/tablets. Content, profiles, and linked websites must be optimized for mobile viewing (key to 'Mobile' in SMAC and Mobile SEO).
- Example: Bakery ensures its Instagram photos are clear on small screens and links to a mobile-friendly online ordering page.


No Comments