Mobile Marketing: Strategy & Key Considerations
Developing a Basic Mobile Strategy:
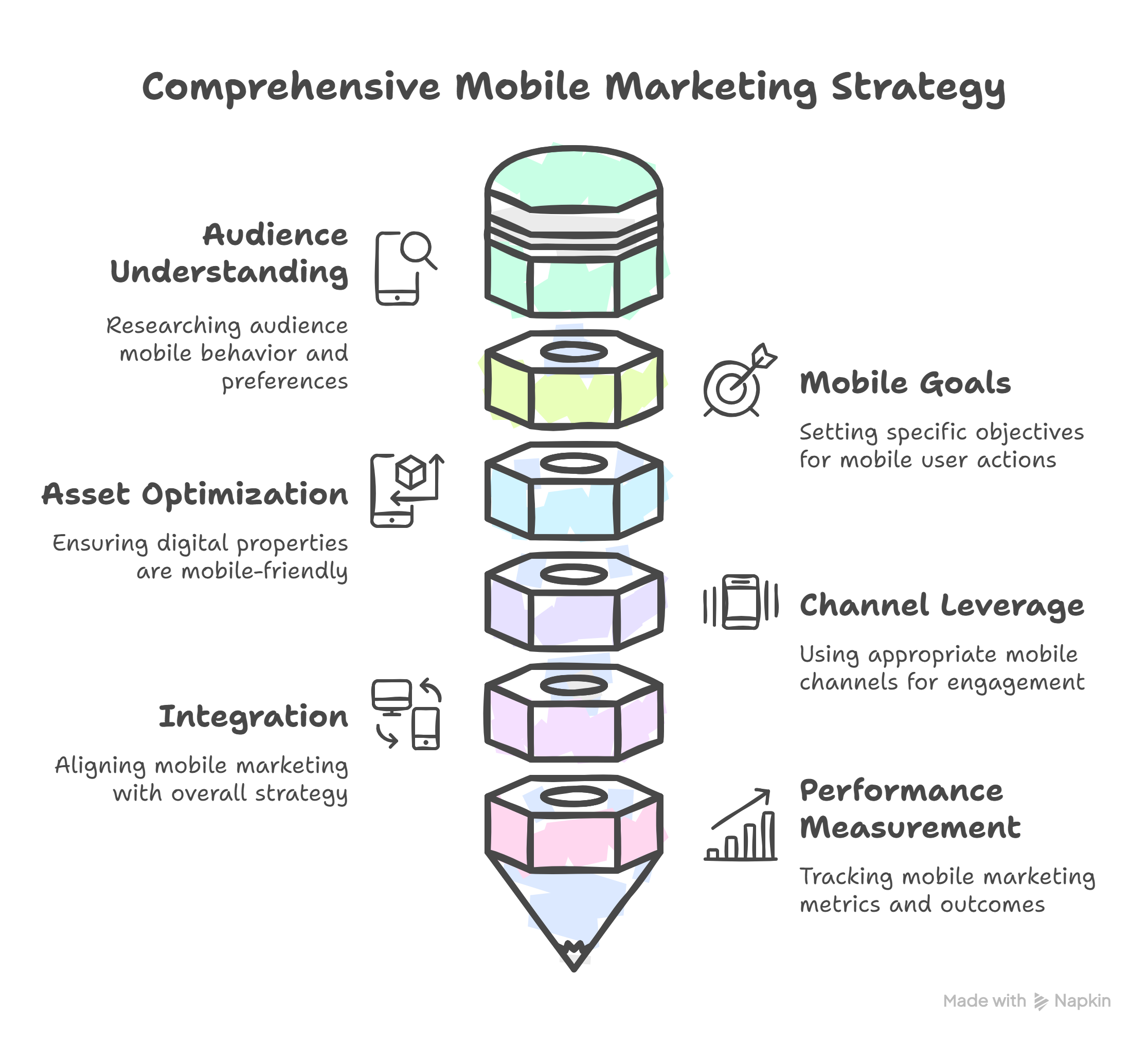
Creating a mobile strategy ensures your efforts are focused and effective in reaching users on their preferred devices.
-
Understand Your Audience's Mobile Behavior:
- Explanation: Research how your target audience uses their smartphones and tablets. What apps do they use? When are they most active? Do they prefer browsing websites, using apps, or engaging on social media via mobile?
- Example: A B2B software company realizes its target audience primarily uses LinkedIn and checks email on mobile during commutes but researches complex solutions on desktop later. Their mobile strategy might focus on concise LinkedIn updates and mobile-friendly emails, driving users to desktop-optimized resources.
-
Set Mobile-Specific Goals:
- Explanation: Define what you want users to achieve specifically on their mobile devices. These might differ from desktop goals. Examples include driving app downloads, generating phone calls (click-to-call), encouraging physical store visits (via maps), enabling mobile purchases, or increasing engagement within a mobile app.
- Example: A local pizza restaurant sets a goal: "Increase online orders placed via our mobile website by 20% this quarter."
-
Optimize Core Assets for Mobile:
-
Explanation: Ensure your foundational digital properties work flawlessly on mobile.
- Website: Must have a responsive design (adapts to screen size), load quickly, and feature easy navigation (large buttons, simple menus - "thumb-friendly").
- Email: Use mobile-friendly templates (single column, readable font size), keep copy concise, and make CTAs (Call-to-Action buttons) easy to tap.
- Example: An e-commerce site ensures product images load fast on mobile, the checkout process has large form fields, and buttons like "Add to Cart" are prominent and easy to press on a touchscreen.
-
Explanation: Ensure your foundational digital properties work flawlessly on mobile.
-
Leverage Relevant Mobile Channels:
- Explanation: Based on your audience and goals, choose the most appropriate mobile channels. This could include mobile-optimized search ads (Mobile SEM), SMS/MMS campaigns for promotions or alerts, developing a dedicated mobile app, running ads within other apps (in-app advertising), focusing on mobile social media, or using location-based tactics.
- Example: A concert venue uses SMS alerts (with opt-in) to notify ticket holders of last-minute changes, promotes upcoming shows heavily on mobile social media (Instagram, Facebook), and ensures its website's event calendar is easy to browse on a phone.
-
Integrate with Overall Marketing:
- Explanation: Mobile marketing shouldn't exist in a silo. Ensure a consistent brand message and user experience whether the customer interacts with you on mobile, desktop, or even offline. Data should ideally be shared across channels for a unified customer view (omnichannel approach).
- Example: A user starts browsing for a hotel on their phone via a social media ad, later receives a reminder email on their desktop, and can complete the booking easily on either device with a consistent interface.
-
Measure Mobile Performance:
- Explanation: Track metrics specific to your mobile efforts. Monitor mobile website traffic and conversion rates (using tools like Google Analytics), track app downloads and in-app engagement, analyze SMS open and click rates, and assess the performance of mobile ad campaigns.
- Example: The pizza restaurant tracks how many users access their website via mobile vs. desktop, the conversion rate for orders placed on mobile, and the click-through rate on their mobile search ads promoting delivery.
Key Considerations for Mobile Marketing:
- Screen Size: Design interfaces and content recognizing the limited space. Prioritize key information and ensure readability.
- Conciseness: Mobile users often scan quickly. Keep text messages, push notifications, and on-screen copy brief and impactful.
- Speed: Mobile users have low tolerance for slow loading times. Optimize images, website code, and app performance for speed.
- Context: Think about when and where users might be interacting on mobile (e.g., on the go, during short breaks). Tailor messages and experiences accordingly (e.g., quick actions vs. deep research).
- Permissions & Privacy: Absolutely critical. Always get explicit user consent (opt-in) before sending SMS messages or push notifications, or accessing location data. Clearly explain why you need the data and provide easy opt-out options.

No Comments