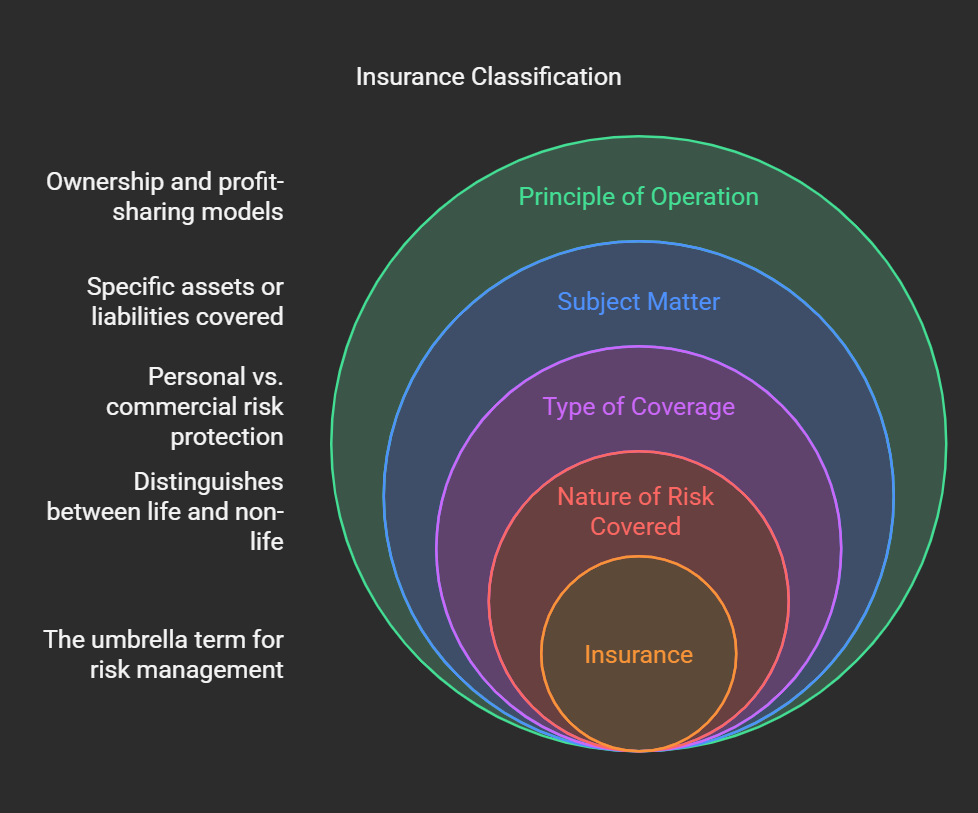
Classification of insurance
Insurance can be classified in several ways, depending on the criteria used. Here's a breakdown of the most common classifications:
- By the Nature of the Risk Covered:
Life Insurance: Covers the risk of financial loss due to death. Non-Life Insurance (General Insurance): Covers risks other than death, such as property damage, liability, and health.
- By the Type of Coverage:
Personal Insurance: Covers risks related to individuals and their families, such as life insurance, health insurance, and homeowners insurance. Commercial Insurance: Covers risks related to businesses, such as property insurance, liability insurance, and workers' compensation.
- By the Subject Matter:
Property Insurance: Covers risks related to physical assets, such as homes, vehicles, and businesses. Liability Insurance: Covers risks related to legal obligations to others, such as bodily injury or property damage. Health Insurance: Covers risks related to medical expenses. Marine Insurance: Covers risks related to the transportation of goods by sea. Aviation Insurance: Covers risks related to aircrafts. Miscellaneous Insurance: This category covers all other forms of insurance that do not fit into the other categories.
- By the Principle of Operation:
Mutual Insurance: Owned by the policyholders, who share in the profits or losses of the company. Stock Insurance: Owned by stockholders, who receive profits or bear losses.
- By the Duration of Coverage:
Term Insurance: Provides coverage for a specific period. Permanent Insurance: Provides lifelong coverage.
- By the Requirement of Law:
Mandatory Insurance: Required by law, such as auto liability insurance. Voluntary Insurance: Optional insurance purchased by individuals or businesses. These classifications help to organize and understand the diverse range of insurance products available.

No Comments