Structure of Financial System
The financial system is a complex network of institutions, markets, and instruments that facilitate the flow of funds between savers and borrowers. Here's a breakdown of its key components:
1. Financial Institutions:
-
Banks:
- Commercial banks (e.g., Chase, Bank of America)
- Investment banks (e.g., Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley)
- Savings and loan associations
- Credit unions
-
Insurance Companies:
- Life insurance companies
- Property and casualty insurance companies
-
Investment Funds:
- Mutual funds
- Hedge funds
- Pension funds
-
Non-bank Financial Institutions:
- Finance companies
- Leasing companies
- Mortgage companies
2. Financial Markets:
-
Money Market: Deals with short-term debt instruments (less than one year).
- Examples: Treasury bills, commercial paper
-
Capital Market: Deals with long-term debt and equity instruments.
- Examples: Stocks, bonds, mortgages
3. Financial Instruments:
-
Debt Instruments:
- Bonds (issued by governments and corporations)
- Loans (mortgages, car loans)
- Bills (short-term debt instruments)
-
Equity Instruments:
- Stocks (represent ownership in a company)
-
Derivatives:
- Options, futures, swaps (contracts based on underlying assets)
4. Financial Services:
- Lending
- Borrowing
- Investing
- Insurance
- Payment processing
- Financial advice
5. Regulatory Framework:
- Central banks (e.g., Federal Reserve in the US)
- Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
- Financial Stability Oversight Council (FSOC)
How it Works:
- Savers deposit their money in banks, purchase bonds, or invest in stocks.
- Borrowers obtain funds from banks, issue bonds, or sell stock.
- Financial institutions act as intermediaries, connecting savers and borrowers.
- Financial markets provide a platform for the buying and selling of financial instruments.
- Regulatory bodies ensure the stability and integrity of the financial system.
Key Functions of the Financial System:
- Efficient allocation of capital: Directing funds to the most productive investments.
- Price discovery: Determining the fair value of financial assets.
- Risk management: Helping individuals and businesses manage financial risks.
-
Economic growth: Supporting economic activity by facilitating investment and innovation.
Financial Services
Lending
Financial Institutions
Borrowing
Investing
Banks
Insurance
Insurance Companies
Payment Processing
Investment Funds
Financial Advice
Non-bank Financial Institutions
Financial System
Regulatory Framework
Financial Instruments
Central Banks
Debt Instruments
Securities and Exchange Commission
Equity Instruments
Derivatives
Financial Stability Oversight Council
Financial Markets
Money Market
Capital Market
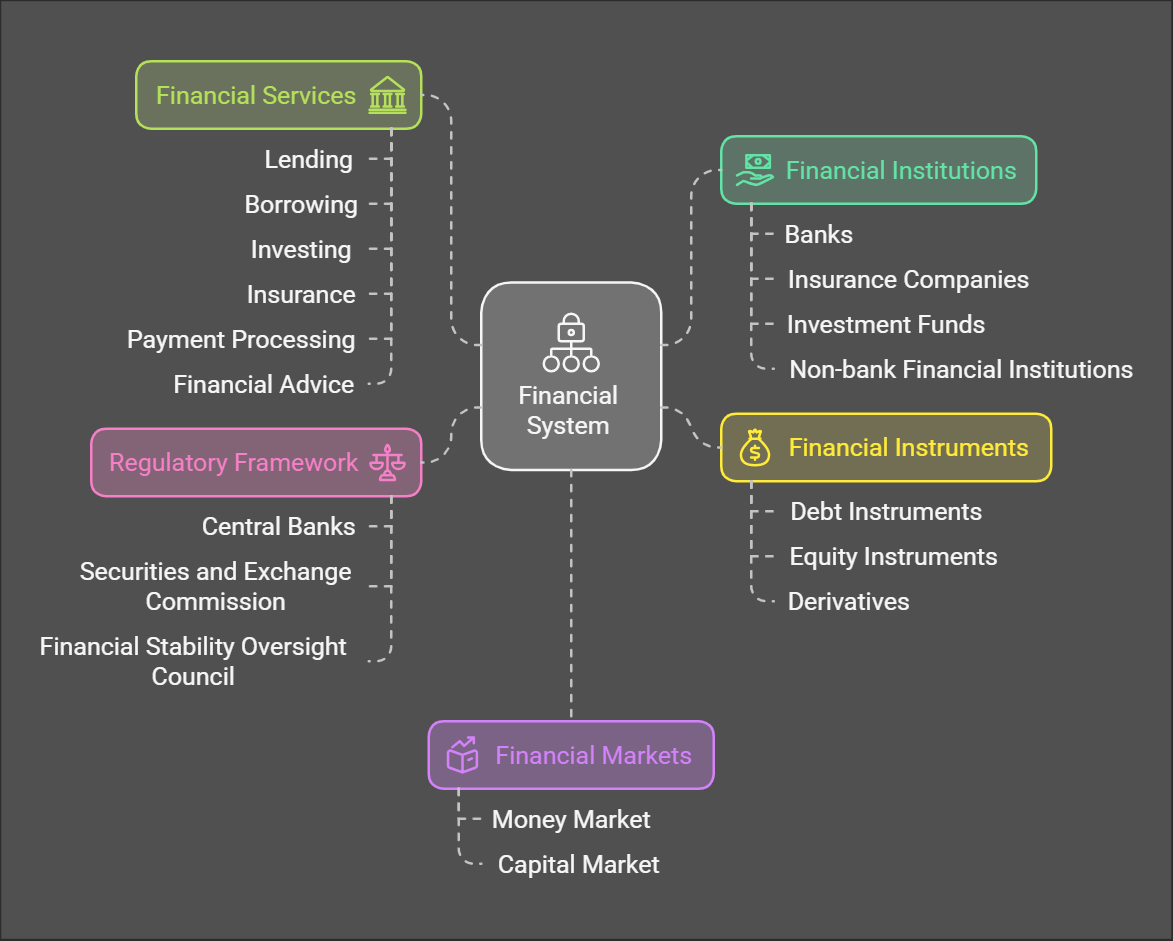 This structure illustrates how the various components of the financial system interact to facilitate the flow of funds and support economic growth.
This structure illustrates how the various components of the financial system interact to facilitate the flow of funds and support economic growth.

No Comments