Framework for establishing valid knowledge, through Nyaya system
Here we will try to understand the Nyaya Darshana's framework for knowledge creation, highlighting its comprehensive approach to establishing valid knowledge.
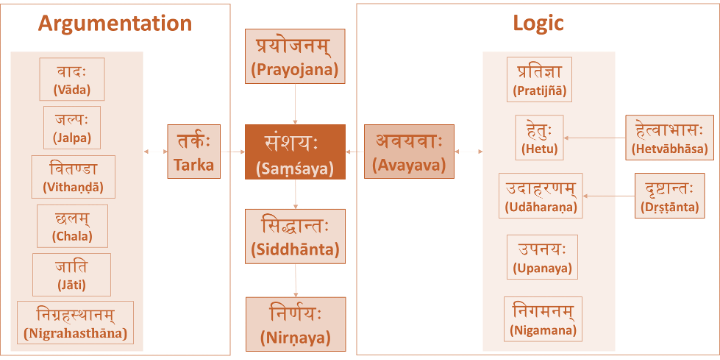
Key Elements of Knowledge Creation
Nyaya identifies several crucial elements in the knowledge creation process:
- Definite objects of knowledge (Prameyas): These are the entities or topics about which knowledge is sought.
- Legitimate means of inquiry (Pramāṇas): These are the valid methods for acquiring knowledge, including perception, inference, comparison, and testimony.
- Legitimate doubt (Saṃśaya): Doubt or ambiguity in existing knowledge is essential for initiating the knowledge creation process.
Nyaya's Framework for Knowledge Creation
Nyaya's framework is robust and includes psychological, procedural, and logical aspects.
Psychological Features
- Prayojana (End Insight): This refers to the purpose or goal that drives the knowledge creation exercise.
- Saṃśaya (Doubt): This is the ambiguity or uncertainty that motivates the search for new knowledge.
- Siddhanta (Tenant): This is a confirmed conclusion or established knowledge that resolves the doubt.
- Nirnaya (Bank of Knowledge): This is the existing body of accepted knowledge, which is updated with new Siddhanta.
Procedural Aspect
- Argumentation: In an oral tradition, knowledge creation primarily occurs through discussions and debates.
-
Types of Arguments: Nyaya classifies arguments into three types:
- Vāda: A constructive dialogue aimed at searching for the truth.
- Jalpa: An argument where each party aims to establish their own proposition, potentially using tricks.
- Vitandā: An argument where one party aims to refute the opponent without having their own thesis.
Logical Aspect
- Systematic Procedure: Arguments must follow a logical structure, including setting out hypotheses, providing reasons, and avoiding fallacies.
Conclusion
Nyaya's framework for knowledge creation offers a comprehensive approach that integrates psychological, procedural, and logical aspects. It emphasizes the importance of doubt, systematic inquiry, and rigorous argumentation in establishing valid knowledge. This framework provides valuable insights for understanding the process of knowledge creation and validation in Nyaya philosophy.

No Comments